建图,链式前向星,拓扑排序
基本介绍
有向 vs 无向、不带权 vs 带权,入参一般为节点数量 n 和所有的边 或者直接给图
建图的三种方式
(1)邻接矩阵(适合点的数量不多的图)
(2)邻接表(最常用的方式)
(3)链式前向星(空间要求严苛情况下使用。比赛必用,大厂笔试、面试不常用)
Tip
【必备】课程里涉及图的内容:建图、链式前向星、拓扑排序、最小生成树、bfs、双向广搜、最短路(Dijkstra、A*、Floyd、Bellman-Ford、SPFA)
【挺难】课程里涉及图的内容:基环树、欧拉回路、割点和桥、强连通分量、双连通分量、最大流、费用流、二分图的最大匹配
邻接矩阵建图
基本介绍
通过二维矩阵存储图,graph [ i ] [ j ] 表示 i 与 j 的联系,也可以表示权值
无向图是特殊的有向图,则 graph [ i ] [ j ] 与 graph [ j ] [ i ] 都要设置
代码实现
java
public class Main {
// 点的最大数量
public static int MAXN = 11;
// 邻接矩阵方式建图
public static int[][] graph1 = new int[MAXN][MAXN];
public static void build(int n) {
// 邻接矩阵清空
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
graph1[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// 邻接矩阵建立有向图带权图
public static void directGraph(int[][] edges) {
for (int[] edge : edges) {
graph1[edge[0]][edge[1]] = edge[2];
}
}
// 邻接矩阵建立无向图带权图
public static void undirectGraph(int[][] edges) {
// 邻接矩阵建图
for (int[] edge : edges) {
graph1[edge[0]][edge[1]] = edge[2];
graph1[edge[1]][edge[0]] = edge[2];
}
}
public static void traversal(int n) {
System.out.println("邻接矩阵遍历 :");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
System.out.print(graph1[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 理解了带权图的建立过程,也就理解了不带权图
// 点的编号为 1...n
// 例子 1 自己画一下图,有向带权图,然后打印结果
int n1 = 4;
int[][] edges1 = {{1, 3, 6}, {4, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {2, 3, 5}, {3, 1, 1}};
build(n1);
directGraph(edges1);
traversal(n1);
System.out.println("==============================");
// 例子 2 自己画一下图,无向带权图,然后打印结果
int n2 = 5;
int[][] edges2 = {{3, 5, 4}, {4, 1, 1}, {3, 4, 2}, {5, 2, 4}, {2, 3, 7}, {1, 5, 5}, {4, 2, 6}};
build(n2);
undirectGraph(edges2);
traversal(n2);
}
}
/*
输出结果如下
邻接矩阵遍历 :
0 7 6 0
0 0 5 2
1 0 0 0
0 0 4 0
==============================
邻接矩阵遍历 :
0 0 0 1 5
0 0 7 6 4
0 7 0 2 4
1 6 2 0 0
5 4 4 0 0
*/邻接表建图
基本介绍
邻接表采用数组 + 单向链表的结构,数组中每个元素节点后挂架一个链表,表示与该元素相连的元素都存储在链表中,同样分有权与无权图,若是有权图,链表中的值可以采用数组来存储
代码实现
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
// 点的最大数量
public static int MAXN = 11;
// 邻接表方式建图
// public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph2 = new ArrayList<>();
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<int[]>> graph2 = new ArrayList<>();
public static void build(int n) {
// 邻接表清空和准备
graph2.clear();
// 下标需要支持 1 ~ n,所以加入 n + 1 个列表,0下标准备但不用
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph2.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
public static void directGraph(int[][] edges) {
// 邻接表建图
for (int[] edge : edges) {
// graph2.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
graph2.get(edge[0]).add(new int[] { edge[1], edge[2] });
}
}
public static void undirectGraph(int[][] edges) {
// 邻接表建图
for (int[] edge : edges) {
// graph2.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
// graph2.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
graph2.get(edge[0]).add(new int[] { edge[1], edge[2] });
graph2.get(edge[1]).add(new int[] { edge[0], edge[2] });
}
}
public static void traversal(int n) {
System.out.println("邻接表遍历 :");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.print(i + "(邻居、边权) : ");
for (int[] edge : graph2.get(i)) {
System.out.print("(" + edge[0] + "," + edge[1] + ") ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 理解了带权图的建立过程,也就理解了不带权图
// 点的编号为 1...n
// 例子 1 自己画一下图,有向带权图,然后打印结果
int n1 = 4;
int[][] edges1 = { { 1, 3, 6 }, { 4, 3, 4 }, { 2, 4, 2 }, { 1, 2, 7 }, { 2, 3, 5 }, { 3, 1, 1 } };
build(n1);
directGraph(edges1);
traversal(n1);
System.out.println("==============================");
// 例子 2 自己画一下图,无向带权图,然后打印结果
int n2 = 5;
int[][] edges2 = { { 3, 5, 4 }, { 4, 1, 1 }, { 3, 4, 2 }, { 5, 2, 4 }, { 2, 3, 7 }, { 1, 5, 5 }, { 4, 2, 6 } };
build(n2);
undirectGraph(edges2);
traversal(n2);
}
}
/*
输出结果如下
邻接表遍历 :
1(邻居、边权) : (3,6) (2,7)
2(邻居、边权) : (4,2) (3,5)
3(邻居、边权) : (1,1)
4(邻居、边权) : (3,4)
==============================
邻接表遍历 :
1(邻居、边权) : (4,1) (5,5)
2(邻居、边权) : (5,4) (3,7) (4,6)
3(邻居、边权) : (5,4) (4,2) (2,7)
4(邻居、边权) : (1,1) (3,2) (2,6)
5(邻居、边权) : (3,4) (2,4) (1,5)
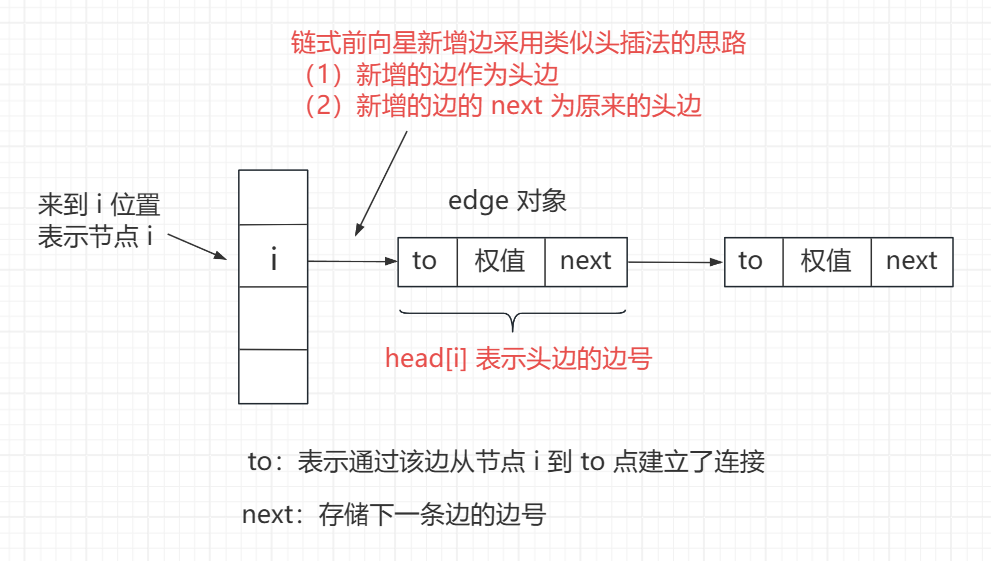
*/链式前向星建图
基本介绍
链式前向星可以理解为是对邻接表的扩展,邻接表中每个单链表中存储的元素是动态变化的,空间大小是不确定的,而链式前向星在单链表中存储的不再是每一个点,存储的是边对象
head 数组:下标表示点的编号,值表示该点位置处链接的头边对应的边号
next 数组:下标表示边号,值表示下一条边的边号
to 数组:下标表示边号,值表示去往的点
weight 数组:下标表示边号,值表示权重
cnt 变量:表示当前边对应的边号
代码实现
java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
// 点的最大数量
public static int MAXN = 11;
// 边的最大数量
// 只有链式前向星方式建图需要这个数量
// 注意如果无向图的最大数量是 m 条边,数量要准备 m*2
// 因为一条无向边要加两条有向边
public static int MAXM = 21;
// 链式前向星方式建图
public static int[] head = new int[MAXN];
public static int[] next = new int[MAXM];
public static int[] to = new int[MAXM];
// 如果边有权重,那么需要这个数组
public static int[] weight = new int[MAXM];
// 如果加入一条边,则当前的边是 cnt 号边,cnt++
public static int cnt;
public static void build(int n) {
// 链式前向星清空
cnt = 1;
// 下标需要支持 1 ~ n,0下标准备但不用
Arrays.fill(head, 1, n + 1, 0);
}
// 链式前向星加边
public static void addEdge(int u, int v, int w) {
// u -> v , 边权重是 w
next[cnt] = head[u];
to[cnt] = v;
weight[cnt] = w;
head[u] = cnt++;
}
public static void directGraph(int[][] edges) {
// 链式前向星建图
for (int[] edge : edges) {
addEdge(edge[0], edge[1], edge[2]);
}
}
public static void undirectGraph(int[][] edges) {
// 链式前向星建图
for (int[] edge : edges) {
addEdge(edge[0], edge[1], edge[2]);
addEdge(edge[1], edge[0], edge[2]);
}
}
public static void traversal(int n) {
System.out.println("链式前向星 :");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.print(i + "(邻居、边权) : ");
// 注意这个 for 循环,链式前向星的方式遍历
for (int ei = head[i]; ei > 0; ei = next[ei]) {
System.out.print("(" + to[ei] + "," + weight[ei] + ") ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 理解了带权图的建立过程,也就理解了不带权图
// 点的编号为 1...n
// 例子 1 自己画一下图,有向带权图,然后打印结果
int n1 = 4;
int[][] edges1 = {{1, 3, 6}, {4, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {2, 3, 5}, {3, 1, 1}};
build(n1);
directGraph(edges1);
traversal(n1);
System.out.println("==============================");
// 例子 2 自己画一下图,无向带权图,然后打印结果
int n2 = 5;
int[][] edges2 = {{3, 5, 4}, {4, 1, 1}, {3, 4, 2}, {5, 2, 4}, {2, 3, 7}, {1, 5, 5}, {4, 2, 6}};
build(n2);
undirectGraph(edges2);
traversal(n2);
}
}
/*
输出结果如下
链式前向星 :
1(邻居、边权) : (2,7) (3,6)
2(邻居、边权) : (3,5) (4,2)
3(邻居、边权) : (1,1)
4(邻居、边权) : (3,4)
==============================
链式前向星 :
1(邻居、边权) : (5,5) (4,1)
2(邻居、边权) : (4,6) (3,7) (5,4)
3(邻居、边权) : (2,7) (4,2) (5,4)
4(邻居、边权) : (2,6) (3,2) (1,1)
5(邻居、边权) : (1,5) (2,4) (3,4)
*/拓扑排序
基本介绍
每个节点的前置节点都在这个节点之前,要求:有向图、没有环
拓扑排序的顺序可能不只一种。拓扑排序也可以用来判断有没有环
(1)在图中找到所有入度为 0 的点
(2)把所有入度为 0 的点在图中删掉,重点是删掉影响!继续找到入度为 0 的点并删掉影响
(3)直到所有点都被删掉,依次删除的顺序就是正确的拓扑排序结果
(4)如果无法把所有的点都删掉,说明有向图里有环
模板题
力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/course-schedule-ii/description/
牛客:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/88f7e156ca7d43a1a535f619cd3f495c
邻接表建图-力扣
java
class Solution {
public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
// 采用邻接表建图
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
int[] inDegree = new int[numCourses];
for (int[] edge : prerequisites) {
// 注意依赖关系,想要学习课程 0 ,需要先完成课程 1
graph.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
// 记录每个节点的入度
inDegree[edge[0]]++;
}
// 数组实现队列,常数时间更好
int[] queue = new int[numCourses];
int l = 0;
int r = 0;
// 找到入度为 0 的节点,将该节点加入队列
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (inDegree[i] == 0) {
queue[r++] = i;
}
}
// 收集入度为 0 的节点个数,如果与总结点数不同,则存在环
int cnt = 0;
while (l < r) {
// 取出队头元素。消除对与其相连节点的影响
int cur = queue[l++];
cnt++;
for (int next : graph.get(cur)) {
// 消除影响,更新入度
inDegree[next]--;
if (inDegree[next] == 0) {
queue[r++] = next;
}
}
}
// 根据题目要求,如果存在环,就返回一个空数组
return cnt == numCourses ? queue : new int[0];
}
}邻接表建图-牛客
java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StreamTokenizer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static int MAXN = 200001;
// 拓扑排序,用到队列
public static int[] queue = new int[MAXN];
public static int l, r;
// 拓扑排序,入度表
public static int[] indegree = new int[MAXN];
// 收集拓扑排序的结果
// ans 无需清空,再后续的测试中会将脏数据覆盖
public static int[] ans = new int[MAXN];
public static int n, m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StreamTokenizer in = new StreamTokenizer(br);
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
while (in.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF) {
n = (int) in.nval;
in.nextToken();
m = (int) in.nval;
// 动态建图,比赛肯定不行,但是一般大厂笔试、面试允许
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
Arrays.fill(indegree, 0, n + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0, from, to; i < m; i++) {
in.nextToken();
from = (int) in.nval;
in.nextToken();
to = (int) in.nval;
graph.get(from).add(to);
indegree[to]++;
}
if (!topoSort(graph)) {
out.println(-1);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
out.print(ans[i] + " ");
}
out.println(ans[n - 1]);
}
}
out.flush();
out.close();
br.close();
}
// 有拓扑排序返回true
// 没有拓扑排序返回false
public static boolean topoSort(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph) {
l = r = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
queue[r++] = i;
}
}
int fill = 0;
while (l < r) {
int cur = queue[l++];
ans[fill++] = cur;
for (int next : graph.get(cur)) {
if (--indegree[next] == 0) {
queue[r++] = next;
}
}
}
return fill == n;
}
}链式前向星建图-牛客
java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StreamTokenizer;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static int MAXN = 200001;
public static int MAXM = 200001;
// 建图相关,链式前向星
public static int[] head = new int[MAXN];
public static int[] next = new int[MAXM];
public static int[] to = new int[MAXM];
public static int cnt;
// 拓扑排序,用到队列
public static int[] queue = new int[MAXN];
public static int l, r;
// 拓扑排序,入度表
public static int[] indegree = new int[MAXN];
// 收集拓扑排序的结果
public static int[] ans = new int[MAXN];
public static int n, m;
public static void build(int n) {
cnt = 1;
Arrays.fill(head, 0, n + 1, 0);
Arrays.fill(indegree, 0, n + 1, 0);
}
// 用链式前向星建图
public static void addEdge(int f, int t) {
next[cnt] = head[f];
to[cnt] = t;
head[f] = cnt++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StreamTokenizer in = new StreamTokenizer(br);
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
while (in.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF) {
n = (int) in.nval;
in.nextToken();
m = (int) in.nval;
build(n);
for (int i = 0, from, to; i < m; i++) {
in.nextToken();
from = (int) in.nval;
in.nextToken();
to = (int) in.nval;
addEdge(from, to);
indegree[to]++;
}
if (!topoSort()) {
out.println(-1);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
out.print(ans[i] + " ");
}
out.println(ans[n - 1]);
}
}
out.flush();
out.close();
br.close();
}
public static boolean topoSort() {
l = r = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
queue[r++] = i;
}
}
int fill = 0;
while (l < r) {
int cur = queue[l++];
ans[fill++] = cur;
// 用链式前向星的方式,遍历 cur 的相邻节点
for (int ei = head[cur]; ei != 0; ei = next[ei]) {
if (--indegree[to[ei]] == 0) {
queue[r++] = to[ei];
}
}
}
return fill == n;
}
}字典序最小的拓扑排序
题目连接
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/U107394
思路分析
本题还是拓扑排序的模板,只不过要求是最小字典序,用小根堆维护即可,并用数组实现堆
代码实现
java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StreamTokenizer;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static int MAXN = 100001;
public static int MAXM = 100001;
// 建图相关,链式前向星
public static int[] head = new int[MAXN];
public static int[] next = new int[MAXM];
public static int[] to = new int[MAXM];
public static int cnt;
// 拓扑排序,不用队列,用小根堆,为了得到字典序最小的拓扑排序
public static int[] heap = new int[MAXN];
public static int heapSize;
// 拓扑排序,入度表
public static int[] indegree = new int[MAXN];
// 收集拓扑排序的结果
public static int[] ans = new int[MAXN];
public static int n, m;
// 清理之前的脏数据
public static void build(int n) {
cnt = 1;
heapSize = 0;
Arrays.fill(head, 0, n + 1, 0);
Arrays.fill(indegree, 0, n + 1, 0);
}
// 用链式前向星建图
public static void addEdge(int f, int t) {
next[cnt] = head[f];
to[cnt] = t;
head[f] = cnt++;
}
// 小根堆里加入数字
public static void push(int num) {
int i = heapSize++;
heap[i] = num;
// heapInsert 的过程
while (heap[i] < heap[(i - 1) / 2]) {
swap(i, (i - 1) / 2);
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
}
// 小根堆里弹出最小值
public static int pop() {
int ans = heap[0];
heap[0] = heap[--heapSize];
// heapify 的过程
int i = 0;
int l = 1;
while (l < heapSize) {
int best = l + 1 < heapSize && heap[l + 1] < heap[l] ? l + 1 : l;
best = heap[best] < heap[i] ? best : i;
if (best == i) {
break;
}
swap(best, i);
i = best;
l = i * 2 + 1;
}
return ans;
}
// 判断小根堆是否为空
public static boolean isEmpty() {
return heapSize == 0;
}
// 交换堆上两个位置的数字
public static void swap(int i, int j) {
int tmp = heap[i];
heap[i] = heap[j];
heap[j] = tmp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StreamTokenizer in = new StreamTokenizer(br);
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
while (in.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF) {
n = (int) in.nval;
in.nextToken();
m = (int) in.nval;
build(n);
for (int i = 0, from, to; i < m; i++) {
in.nextToken();
from = (int) in.nval;
in.nextToken();
to = (int) in.nval;
addEdge(from, to);
indegree[to]++;
}
topoSort();
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
out.print(ans[i] + " ");
}
out.println(ans[n - 1]);
}
out.flush();
out.close();
br.close();
}
public static void topoSort() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
push(i);
}
}
int fill = 0;
while (!isEmpty()) {
int cur = pop();
ans[fill++] = cur;
// 用链式前向星的方式,遍历cur的相邻节点
for (int ei = head[cur]; ei != 0; ei = next[ei]) {
if (--indegree[to[ei]] == 0) {
push(to[ei]);
}
}
}
}
}火星词典
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/Jf1JuT/
思路分析
对于两个单词,能分出胜负说明某一位的字符存在字典序的大小关系,只需要从前往后遍历,看哪一位可以分出胜负,那就将二者建立一条边,最后进行拓扑排序,即可得出字典序的顺序
若出现了 abcd 在前,abc 在后的情况,则视为不符合条件,返回空字符串
代码实现
java
class Solution {
public String alienOrder(String[] words) {
// 入度表
int[] inDegree = new int[26];
// 一开始都认为没有出现过
Arrays.fill(inDegree, -1);
for (String w : words) {
for (int i = 0; i < w.length(); i++) {
// 表示出现过
inDegree[w.charAt(i) - 'a'] = 0;
}
}
// 邻接表建图
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < words.length - 1; i++) {
String cur = words[i];
String next = words[i + 1];
// 定义遍历指针,找出分出胜负的字符,建立一条边
int j = 0;
int len = Math.min(cur.length(), next.length());
while (j < len) {
if (cur.charAt(j) != next.charAt(j)) {
graph.get(cur.charAt(j) - 'a').add(next.charAt(j) - 'a');
inDegree[next.charAt(j) - 'a']++;
// 分出胜负,结束遍历
break;
}
j++;
}
// abcd 在前 abc 在后,不符合题意,返回空串
if (j < cur.length() && j == next.length()) {
return "";
}
}
// 拓扑排序
int[] queue = new int[26];
int l = 0, r = 0;
int kinds = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (inDegree[i] != -1) {
kinds++;
}
if (inDegree[i] == 0) {
queue[r++] = i;
}
}
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
while (l < r) {
int cur = queue[l++];
ans.append((char) (cur + 'a'));
for (int next : graph.get(cur)) {
if (--inDegree[next] == 0) {
queue[r++] = next;
}
}
}
return ans.length() == kinds ? ans.toString() : "";
}
}戳印序列
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/stamping-the-sequence/
思路分析
核心:后面盖的印章会取消前面印章盖的错误的地方,最后盖的印章无人取消,即错误点为 0
从第一个字符开始,每次盖印章的长度,依次移动印章的开头,直到印章末尾到达字符串末尾,在这个过程中统计以每个开头盖下印章产生的错误点,从错误点为 0 的位置开始执行拓扑排序的过程,依次取消错误点,注意不能重复取消,入度点为 0 的点是后盖的
由于错误点为 0 的一定是最后盖的,所以最后收集的答案需要逆序输出
代码实现
java
class Solution {
public int[] movesToStamp(String stamp, String target) {
char[] s = stamp.toCharArray();
char[] t = target.toCharArray();
// 印章的长度
int m = stamp.length();
int n = target.length();
// 每个字符为开头盖下印章的长度,统计错误点
int[] inDegree = new int[n - m + 1];
// 初始默认错误点为印章的长度,即没有一个对的上的
Arrays.fill(inDegree, m);
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
int[] queue = new int[n - m + 1];
int l = 0, r = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - m + 1; i++) {
// i 开头的字符位置盖印章,印章长度为 m
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// i 开头往下数 m 个,依次比对字符串
if (s[j] == t[i + j]) {
// 如果发现错误点为 0,则入队
if (--inDegree[i] == 0) {
queue[r++] = i;
}
} else {
// 该情况说明错误点还存在
// from:错误的位置
// to:i 开头的下标
// 边表示 i+j 这个错误位置影响了 i 这个开头
// 之后印章取消的时候即可对 i 开头中错误的位置取消
// 即体现为 错误的位置 -> i 开头,i 开头的入度减减
graph.get(i + j).add(i);
}
}
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
int[] path = new int[n - m + 1];
int size = 0;
// 拓扑排序
while (l < r) {
int cur = queue[l++];
// 收集答案
path[size++] = cur;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (!visited[cur + i]) {
visited[cur + i] = true;
for (int next : graph.get(cur + i)) {
if (--inDegree[next] == 0) {
queue[r++] = next;
}
}
}
}
}
if (size != n - m + 1) {
return new int[0];
}
// 逆序调整
for (int i = 0, j = size - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
int temp = path[i];
;
path[i] = path[j];
path[j] = temp;
}
return path;
}
}