二叉树高频题-上
层序遍历
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/
思路分析
(1)思路一:BFS + 哈希表
BFS 层序遍历二叉树,哈希表记录每个节点对应的层数,根节点是第 0 层,通过层数进而知道哪些节点需要收集在一个 List 中
(2)思路二:数组实现队列 + 一次处理一层节点
BFS 层序遍历二叉树,在 poll 之前记录队列的大小为 size,表示当前层的节点个数
弹出队头元素,将左右孩子入队,这个过程做 size 次
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 用 map 记录节点所在的层,便于收集节点
HashMap<TreeNode, Integer> levels = new HashMap<>();
queue.add(root);
// 根节点为第 0 层
levels.put(root, 0);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
int level = levels.get(cur);
// 刚开始的时候还没有链表,建出来
if (ans.size() == level) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
ans.get(level).add(cur.val);
// 将左右孩子加入队列,并记录层数
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.add(cur.left);
levels.put(cur.left, level + 1);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.add(cur.right);
levels.put(cur.right, level + 1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}优化实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public static int MAXN = 2001;
public static TreeNode[] queue = new TreeNode[MAXN];
// 定义队头,队尾指针
public static int l, r;
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
l = r = 0;
// 将元素放在 r 位置,r ++
// 即 r 始终指向队尾元素的下一个位置
queue[r++] = root;
// BFS 层序遍历
// 只要队列还有元素就继续
while (l < r) {
// poll 之前先记录队列大小
int size = r - l;
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 取出队头元素,将左右孩子入队,这个过程做 size 次
// 每次循环处理一层元素,最后将 list 加入结果集 ans
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode cur = queue[l++];
list.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) {
queue[r++] = cur.left;
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue[r++] = cur.right;
}
}
ans.add(list);
}
}
return ans;
}
}锯齿形层序遍历
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/
思路分析
采用优化的 BFS 层序遍历,利用 reverse 变量来控制收集元素的顺序
有一点区别:因为是收集元素的顺序不同,所以处理的时候先收集节点,在 BFS 层序处理的时候弹出节点就不收集,接着处理左右孩子节点即可
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public static int MAXN = 2001;
public static TreeNode[] queue = new TreeNode[MAXN];
// 定义队头,队尾指针
public static int l, r;
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
l = r = 0;
queue[r++] = root;
// 用 reverse 变量来控制收集元素的顺序
// false:从左 -> 右收集
// true: 从右 -> 左收集
boolean reverse = false;
while (l < r) {
int size = r - l;
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// false:从左 -> 右收集,l .... r-1,收集 size 个
// true: 从右 -> 左收集,r-1 .... l,收集 size 个
// 左 -> 右:i = i + 1
// 右 -> 左:i = i - 1
for (int i = reverse ? r - 1 : l, j = reverse ? -1 : 1, k = 0; k < size; i += j, k++) {
TreeNode cur = queue[i];
list.add(cur.val);
}
// BFS 层序处理逻辑
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode cur = queue[l++];
// 这里不收集节点,直接处理左右孩子
if (cur.left != null) {
queue[r++] = cur.left;
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue[r++] = cur.right;
}
}
ans.add(list);
// 遍历顺序是交替变换的
reverse = !reverse;
}
}
return ans;
}
}二叉树最大宽度
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree/
题意:按层计算宽度,即该层节点的个数,每一层最左的不空节点到最右的不空节点,中间节点无论是否为空都要计算,返回最大宽度
思路分析
利用二叉树的性质,用下标差值来记录每一层的节点数,每一层拿出最左和最右节点,计算下标差值,就知道该层的最大宽度
额外申请一个队列,同步记录节点对应的下标索引
假定头节点为 1 号节点,对于父节点的下标索引 i
(1)左子节点索引为 2 * i
(2)右子节点索引为 2 * i + 1
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public static int MAXN = 3001;
public static TreeNode[] nodeQueue = new TreeNode[MAXN];
// 额外申请一个队列同步记录节点对应的下标索引
public static long[] indexQueue = new long[MAXN];
public static int l, r;
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
// 从根节点开始,初始宽度为 1
int ans = 1;
l = r = 0;
nodeQueue[r] = root;
// r 始终指向队尾元素的下一个位置
indexQueue[r++] = 1;
while (l < r) {
// 计算本层节点的个数
int size = r - l;
// 计算每层的最大宽度,并更新
ans = Math.max(ans, (int) (indexQueue[r - 1] - indexQueue[l] + 1));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = nodeQueue[l];
long id = indexQueue[l++];
// 注意两个队列使用的是同一个头尾指针
// r++ 应该在队列都更新后执行
if (node.left != null) {
nodeQueue[r] = node.left;
indexQueue[r++] = id * 2;
}
if (node.right != null) {
nodeQueue[r] = node.right;
indexQueue[r++] = id * 2 + 1;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}最大深度
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree
思路分析
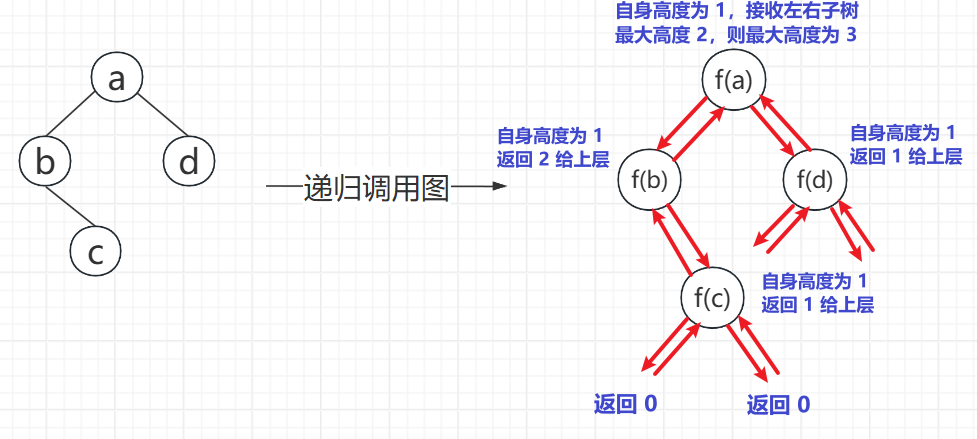
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
// 最大深度 = 本层节点的高度 + 左右子树的最大高度
return root == null ? 0 : Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}最小深度
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
第一种表达:最小深度是指从根节点出发,到所有叶子节点的最小深度
第二种表达:最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量
思路分析
本题仍然可以采用递归的思路,逐层向上返回结果
需要注意的是,如果叶子节点为空,则会返回 0,会干扰最后最小深度的计算结果,再递归前需要先判断
如果叶子节点不为空,再递归
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
// 当前的树是空树
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// 当前 root 是叶子节点,即只有 root 一个节点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
// 设置成最大的目的是不去干扰最后的计算结果
// 因为最后的结果需要取最小
int leftDeep = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int rightDeep = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 如果左右孩子不为空,才递归
// 若为空,返回 0,影响最后的计算结果
if (root.left != null) {
leftDeep = minDepth(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
rightDeep = minDepth(root.right);
}
// 当前层的深度 + 左右孩子的最大深度
// root 算一层,所以要加 1
return Math.min(leftDeep, rightDeep) + 1;
}
}先序序列化与反序列化
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree
思路分析
(1)前序遍历和后序可以实现序列化和反序列化,这里以前序遍历为例,遇到空节点就用 # 标记

(2)中序无法实现序列化和反序列化
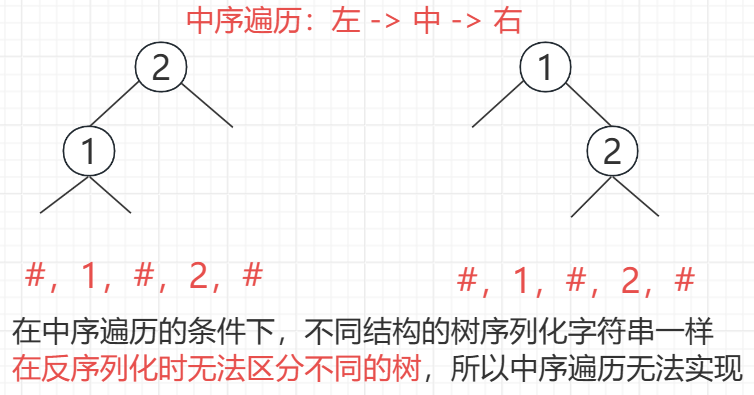
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Codec {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
f(root, builder);
return builder.toString();
}
public void f(TreeNode root, StringBuilder builder) {
// 先序遍历
if (root == null) {
builder.append("#,");
} else {
builder.append(root.val + ",");
f(root.left, builder);
f(root.right, builder);
}
}
// 记录数组消费到哪了
public static int cnt;
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] vals = data.split(",");
cnt = 0;
return g(vals);
}
TreeNode g(String[] vals) {
String cur = vals[cnt++];
if (cur.equals("#")) {
return null;
} else {
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(cur));
head.left = g(vals);
head.right = g(vals);
return head;
}
}
}
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec ser = new Codec();
// Codec deser = new Codec();
// TreeNode ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root));按层序列化与反序列化
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree
思路分析
采用层序遍历,一次处理一个节点的方式实现
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Codec {
public static int MAXN = 10001;
public static TreeNode[] queue = new TreeNode[MAXN];
public static int l, r;
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
if (root != null) {
builder.append(root.val + ",");
l = 0;
r = 0;
queue[r++] = root;
// 层序遍历,一次处理一个节点
while (l < r) {
root = queue[l++];
if (root.left != null) {
builder.append(root.left.val + ",");
queue[r++] = root.left;
} else {
builder.append("#,");
}
if (root.right != null) {
builder.append(root.right.val + ",");
queue[r++] = root.right;
} else {
builder.append("#,");
}
}
}
return builder.toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if (data.equals("")) {
return null;
}
String[] nodes = data.split(",");
int index = 0;
TreeNode root = generate(nodes[index++]);
l = 0;
r = 0;
queue[r++] = root;
while (l < r) {
TreeNode cur = queue[l++];
cur.left = generate(nodes[index++]);
cur.right = generate(nodes[index++]);
if (cur.left != null) {
queue[r++] = cur.left;
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue[r++] = cur.right;
}
}
return root;
}
public TreeNode generate(String val) {
return val.equals("#") ? null : new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(val));
}
}
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec ser = new Codec();
// Codec deser = new Codec();
// TreeNode ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root));先序和中序构造二叉树
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/
思路分析
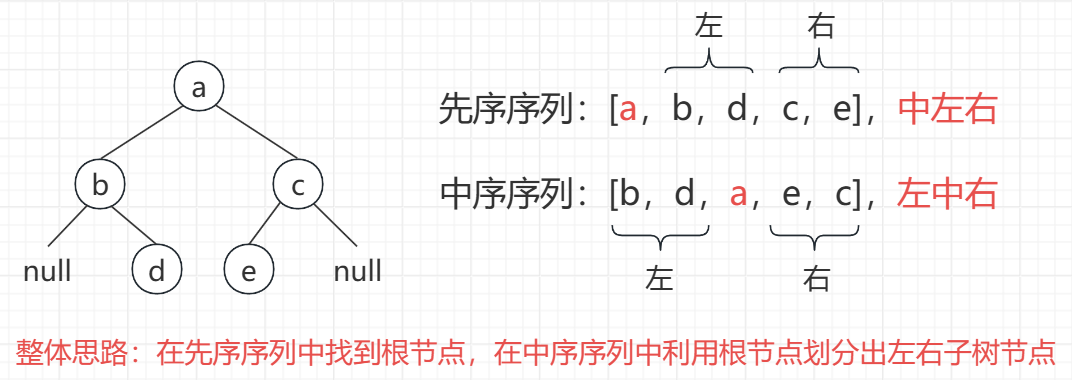
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if (preorder == null || inorder == null || preorder.length != inorder.length) {
return null;
}
// 记录中序遍历每个节点的下标
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return f(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, map);
}
public static TreeNode f(int[] preOrder, int l1, int r1, int[] inOrder, int l2, int r2,
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map) {
if (l1 > r1) {
return null;
}
// 先序遍历顺序:根左右,取出根节点在中序遍历序列中找子节点
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(preOrder[l1]);
// 只有一个节点
if (l1 == r1) {
return head;
}
int k = map.get(preOrder[l1]);
// preOrder : l1(........)[.......r1]
// inOrder : (l2......)k[........r2]
// (...)是左树对应,[...]是右树的对应
// k - l2 表示不包含 k,k 左边的元素个数,即左子树的个数
head.left = f(preOrder, l1 + 1, l1 + (k - l2), inOrder, l2, k - 1, map);
head.right = f(preOrder, l1 + (k - l2) + 1, r1, inOrder, k + 1, r2, map);
return head;
}
}验证完全二叉树
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/check-completeness-of-a-binary-tree/
思路分析
思路:运用 BFS 层序遍历
情况一:有右无左的节点,不是完全二叉树
情况二:发现孩子不全的节点,则其他节点必须全是叶子节点,否则不是完全二叉树
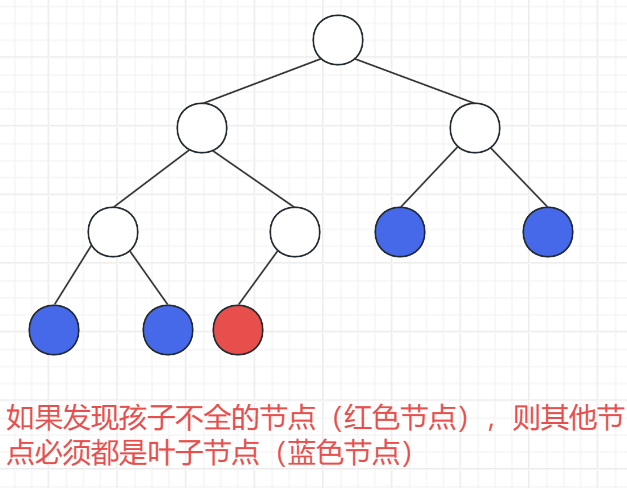
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public static int MAXN = 101;
public static TreeNode[] queue = new TreeNode[MAXN];
public static int l, r;
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
l = r = 0;
queue[r++] = root;
// 是否遇到过左右孩子不双全的节点
boolean leaf = false;
// BFS
while (l < r) {
root = queue[l++];
// 如果没有遇到孩子不双全的节点,leaf = false
// 条件一:判断是否是有右无左
// 若 leaf = true,说明遇到过孩子不双全的节点
// 条件二:此时其他节点都要求是叶子节点,做判断
if (root.left == null && root.right != null || (leaf && (root.left != null || root.right != null))) {
return false;
}
if (root.left != null) {
queue[r++] = root.left;
}
if (root.right != null) {
queue[r++] = root.right;
}
// 遇到了左右孩子不双全的节点,leaf = true
// 若走条件二,则会一直判断是否是叶子节点
if (root.left == null || root.right == null) {
leaf = true;
}
}
return true;
}
}完全二叉树节点个数
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/
思路分析
默认根节点为第 1 层
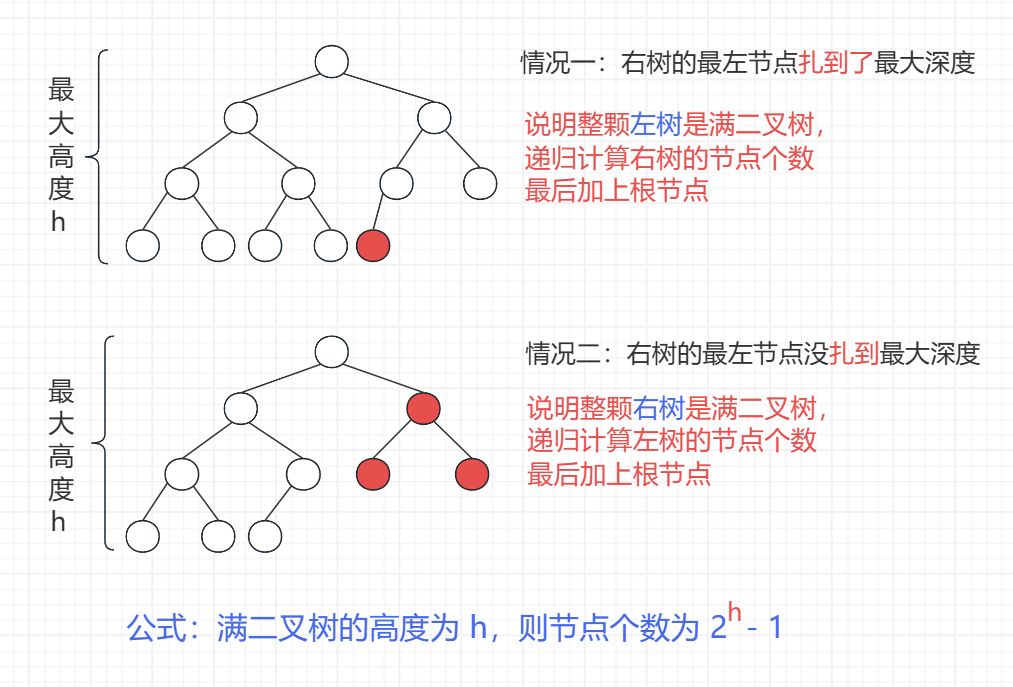
代码实现
时间复杂度:O((log n)2 )
从根节点出发,到右树的最左节点走过了 h 层,接着来到 level + 1 层(h - 1 这么高的层数)继续递归调用左树或者右树
1 + 2 + 3 + ... + n - 1 + n = n * (n + 1)/ 2,规模为 h 的平方,h 是树的高度
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return f(root, 1, mostLeft(root, 1));
}
// cur :当前来到的节点
// level :当前来到的节点在第几层
// h :整颗树的高度,不是 cur 这颗子树的高度
// 求 cur 这颗子树上共有多少个节点
public int f(TreeNode cur, int level, int h) {
if (level == h) {
return 1;
}
// 情况一:cur 的右树扎到 h 层,说明左树是满二叉树
if (mostLeft(cur.right, level + 1) == h) {
return ((1 << (h - level)) - 1 + 1 + f(cur.right, level + 1, h));
} else {
// 情况二:cur 的右树没扎到 h 层,说明右树是满二叉树
// 右树是满二叉树,则层数会比左树是满二叉树少一层
return ((1 << (h - level - 1)) - 1 + 1 + f(cur.left, level + 1, h));
}
}
// 当前节点为 cur,在第 level 层
// 返回从 cur 开始不停向左,能到第几层
public int mostLeft(TreeNode cur, int level) {
while (cur != null) {
level++;
cur = cur.left;
}
// cur 遇到空停,level 多加了一层,要减掉
return level - 1;
}
}