二叉树高频题-下
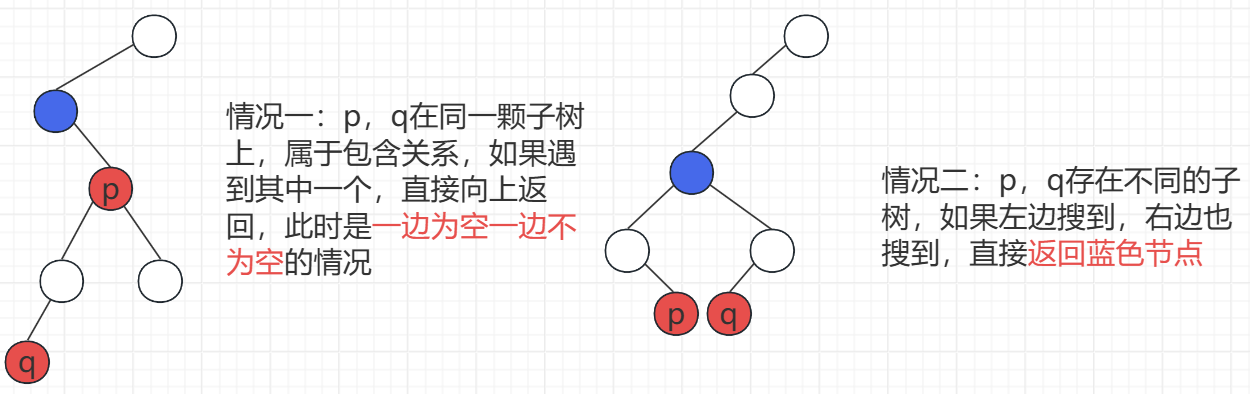
普通二叉树 LCA
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
思路分析
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) {
// root 为空,或者遇到 p,或者遇到 q,返回 root
return root;
}
TreeNode l = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode r = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
// 情况二:左边搜到,右边也搜到,返回 root
if (l != null && r != null) {
return root;
}
if (l == null && r == null) {
return null;
}
// 情况一:p,q 属于包含关系,在同一颗子树上
// 只要遇到一个就返回
// l,r 一个空,一个不为空,返回不空的那个
return l != null ? l : r;
}
}搜索二叉树 LCA
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
思路分析
本题需要利用搜索二叉树的性质,左子树所有节点值 <= 根节点 <= 右子树所有节点值
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
// 搜索二叉树的性质:左子树节点值 < 根节点 < 右子树节点值
// root 从上到下遍历,会有以下 4 种情况,假设 p < q
// 1. p,q 属于同一颗子树,先遇到谁,谁就是答案
// 2. root < p ~ q,root 往右移动
// 3. p ~ q < root,root 往左移动
// 4. p < root < q,root 就是答案
// 先遇到谁返回谁,退出循环
while (root.val != p.val && root.val != q.val) {
// 情况二:p < root < q,root 就是答案,不用搜了,返回
if (Math.min(p.val, q.val) < root.val && root.val < Math.max(p.val, q.val)) {
break;
}
// 情况三、四
root = root.val < Math.min(p.val, q.val) ? root.right : root.left;
}
// 情况一
return root;
}
}累加和为 sum 的所有路径
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/description/
思路分析
典型的递归 + 回溯,递归过程中计算 curSum,并将值作为参数传递,如果符合条件就收集路径
本题要理解清楚递归的执行流程,回溯时,什么情况下要减去 curSum
代码实现
以下代码为更优雅的写法,把 res 和 path 作为递归方法的参数(或局部变量)传递,彻底避免成员变量的依赖,代码可复用性更高
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
traversal(root, targetSum, 0, path, res);
return res;
}
// curSum 表示 cur 节点上方路径的累加和
// 这里传递的是 curSum + cur.val 的计算结果(新值),而非修改原变量
// 左子树递归栈中,拿到的 curSum 是 S + val,但这只是局部副本
// 当左子树递归结束,回到当前层时,上层的 curSum 仍然是原来的 S,没有被修改
// 即回溯时无需对 curSum 进行修改
public void traversal(TreeNode cur, int targetSum, int curSum, List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {
// 递归终止条件,遇到叶子节点,收集路径
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null) {
if (curSum + cur.val == targetSum) {
path.add(cur.val);
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
// 回溯
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
} else {
// 不是叶子节点,继续递归搜索
path.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) {
traversal(cur.left, targetSum, curSum + cur.val, path, res);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
traversal(cur.right, targetSum, curSum + cur.val, path, res);
}
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}验证平衡二叉树
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/balanced-binary-tree
思路分析
平衡二叉树:每个节点的左右子树的高度差值的绝对值 <= 1
递归求解每个节点的子树高度,判断是否符合条件即可
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public static boolean balance;
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
// balance 是全局变量,所有递归过程共享
// 所以每次判断开始时候设置为 true
balance = true;
height(root);
return balance;
}
// 求以 cur 为头的这颗子树的高度
public static int height(TreeNode cur) {
// 如果不平衡,返回什么已经不重要了
if (!balance || cur == null) {
return 0;
}
// 递归求左右子树的高度
int leftHeight = height(cur.left);
int rightHeight = height(cur.right);
// 判断是否是平衡二叉树
if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {
balance = false;
}
// 返回树高,树高 = 当前节点这层高度 + 左右子树的最大高度
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}判断搜索二叉树
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/
思路分析
搜索二叉树:对于每一颗子树,都应该满足左子树所有节点都小于根节点,根节点小于右子树的所有节点
方法一
非递归实现中序遍历,判断是否是升序序列即可
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public static int MAXN = 10001;
public static TreeNode[] stack = new TreeNode[MAXN];
public static int size;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
// 定义前驱指针,用于比较,判断是否升序
TreeNode pre = null;
// size 始终指向栈顶元素的下一个位置
size = 0;
while (size > 0 || root != null) {
// 一直往左
if (root != null) {
stack[size++] = root;
root = root.left;
} else {
// 弹出栈顶元素,处理右子树
root = stack[--size];
// 利用升序特性,判断是否搜索二叉树
if (pre != null && pre.val >= root.val) {
return false;
}
// 移动前驱指针
pre = root;
root = root.right;
}
}
return true;
}
}方法二
利用搜索二叉树的性质,左子树的 max < 根节点 < 右子树的 min
每棵子树的左子树,右子树的最大和最小分别用局部变量接收,将信息返回给子树的根节点
用全局变量 min,max 记录整棵子树的最大和最小,更新全局变量,并将信息向上返回
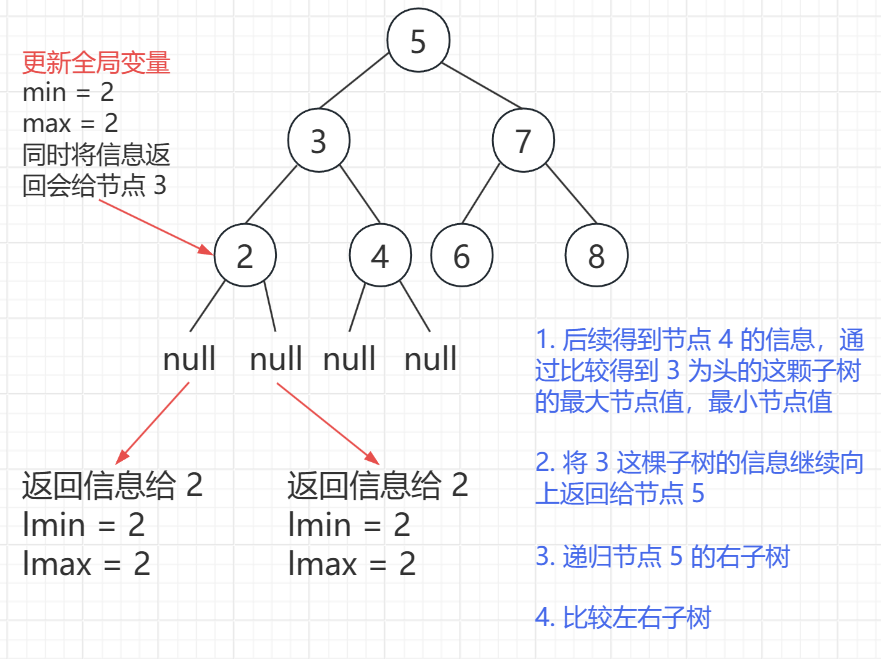
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public static long min;
public static long max;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
// 左子树的 max < 根节点 < 右子树的 min
if (root == null) {
// 这样设置的目的是不让空节点影响判断
// 最小值为最大,最大值为最小
min = Long.MAX_VALUE;
max = Long.MIN_VALUE;
// 空节点符合条件
return true;
}
boolean leftIsValid = isValidBST(root.left);
// 左树的最小和最大
long leftMin = min;
long leftMax = max;
boolean rightIsValid = isValidBST(root.right);
// 右树最小和最大
long rightMin = min;
long rightMax = max;
// 更新当前子树的最小和最大
// 将该信息返回给上游节点
min = Math.min(Math.min(leftMin, rightMin), root.val);
max = Math.max(Math.max(leftMax, rightMax), root.val);
return leftIsValid && rightIsValid && leftMax < root.val && root.val < rightMin;
}
}修建搜索二叉树
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/trim-a-binary-search-tree/
题意:给定范围 [low, high],将二叉树修剪成所有节点都在这个范围内的二叉树
思路分析
利用搜索二叉树的性质,左子树的 max < 根节点 < 右子树的 min
如果 root.val < low,则说明 root 及其左子树的节点都是 < low 的,递归修剪右子树
如果 root.val > high,则说明 root 及其右子树的节点都是 > high 的,递归修剪左子树
否则 root 就是在 low,high 的范围内,递归修剪左右子树并链接,将节点返回即可
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 力扣是 TreeNode root,这里改成 cur 表示当前节点,便于理解
// [left, right] 范围内,左闭右闭区间
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode cur, int low, int high) {
if (cur == null) {
return null;
}
if (cur.val < low) {
return trimBST(cur.right, low, high);
}
if (cur.val > high) {
return trimBST(cur.left, low, high);
}
// left < cur < right
cur.left = trimBST(cur.left, low, high);
cur.right = trimBST(cur.right, low, high);
return cur;
}
}二叉树打家劫舍问题
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber-iii/
思路分析
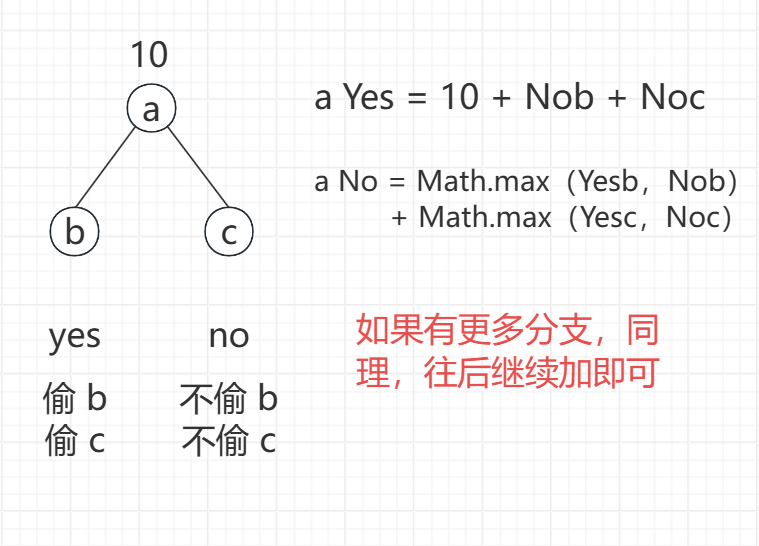
代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int rob(TreeNode root) {
trversal(root);
// 偷头节点和不偷头节点两个情况取最大值
return Math.max(yes, no);
}
// 全局变量,完成了 X 子树的遍历,返回之后
// yes 变成 X 子树在偷头节点的情况下的最大收益
public static int yes;
// 全局变量,完成了 X 子树的遍历,返回之后
// no 变成 X 子树在不偷头节点的情况下的最大收益
public static int no;
public void trversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
yes = 0;
no = 0;
} else {
// 初始变量
// 偷头节点,初始为 root.val
int y = root.val;
// 不偷头节点,初始为 0
int n = 0;
// 递归左子树
trversal(root.left);
// 偷头节点,子树的头节点不能偷
// 则加上不偷子树头节点的价值
y += no;
// 不偷头节点,那子树的头节点可偷可不偷
// 取最大价值
n += Math.max(yes, no);
// 同理递归右子树
trversal(root.right);
y += no;
n += Math.max(yes, no);
// 更新全局变量,向上返回
yes = y;
no = n;
}
}
}