数据结构设计高频题
setAll 功能的哈希表
题目链接
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/7c4559f138e74ceb9ba57d76fd169967
使用 O(1)的操作将哈希表中的 value 值全部设置为 newValue,不能遍历哈希表
思路分析
使用两个变量:setAllValue、setAllTime,加
用一个 setAllTime 变量记录 setAll 的时间,每一个元素都有一个对应的操作时间,如果操作时间小于 setAllTime,则说明改元素会被设置成 setAllValue,返回 setAllValue 即可,否则返回原来的值
代码实现
java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
// key,[value,time],time 表示操作次数
public static HashMap<Integer, int[]> map = new HashMap<>();
public static int setAllValue;
public static int setAllTime;
// 记录每一个元素的操作时间
public static int cnt;
public static void put(int k, int v) {
// 如果 key 存在就更新 value,否则新增
if (map.containsKey(k)) {
int[] value = map.get(k);
value[0] = v;
value[1] = cnt++;
} else {
map.put(k, new int[]{v, cnt++});
}
}
public static void setAll(int v) {
setAllValue = v;
setAllTime = cnt++;
}
public static int get(int k) {
// 判断是否存在
if (!map.containsKey(k)) {
return -1;
}
// 存在,需要判断是返回 value 还是 setAllValue
int[] value = map.get(k);
if (value[1] > setAllTime) {
return value[0];
} else {
return setAllValue;
}
}
// 定义变量接收输入
public static int n, opt, a, b;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StreamTokenizer in = new StreamTokenizer(br);
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
while (in.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF) {
// 在每一轮循环中的得出一个答案,先放到缓冲区
// 所以每次循环开始先要重置一下变量的值
map.clear();
setAllValue = 0;
setAllTime = -1;
cnt = 0;
n = (int) in.nval;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
in.nextToken();
opt = (int) in.nval;
// 若 opt = 1,put 操作
// 若 opt = 2,get 操作
// 若 opt = 3,setAll 操作
if (opt == 1) {
in.nextToken();
a = (int) in.nval;
in.nextToken();
b = (int) in.nval;
put(a, b);
} else if (opt == 2) {
in.nextToken();
a = (int) in.nval;
out.println(get(a));
} else {
in.nextToken();
a = (int) in.nval;
setAll(a);
}
}
}
out.flush();
out.close();
br.close();
}
}LRU 缓存
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lru-cache
什么是 LRU
指定一个 capacity,存储的元素个数上限为 capacity,以 capacity = 3 举例
每一个元素是 key - value 的键值对结构,同时每个元素对应一个操作时间
只要对某个元素操作,则当前元素的操作时间就是最晚的,同时更新其余两个元素的操作时间
如果已经满了,还需要添加元素,则移除操作时间最早的元素
若添加的元素的 key 在缓存中已经存在,则会更新 value,同时更新三个元素的操作时间
思路分析
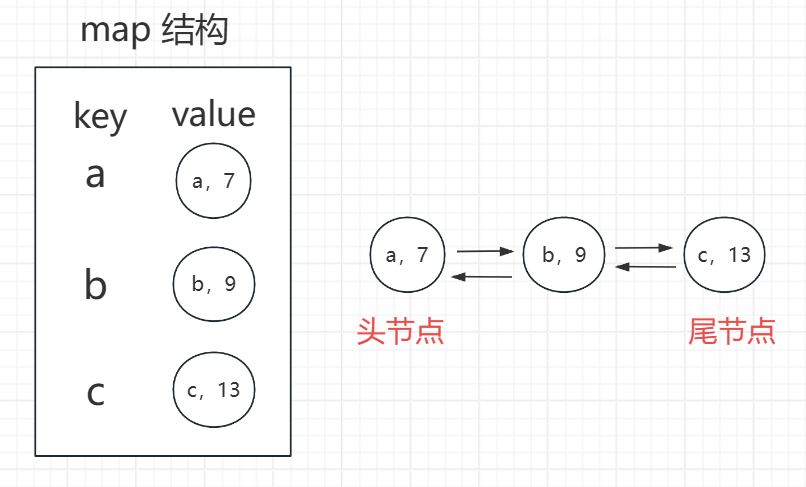
实现结构:哈希表(map 结构:key - 节点地址) + 双向链表
定义头尾指针,头节点指向操作时间最早的节点,尾节点指向操作时间最晚的节点
当对节点操作时,哈希表中做相应的更新,同时调整双向链表,维持元素操作的相对时序
代码实现
java
class LRUCache {
class DoubleNode {
// 每一个元素是 key - value 的结构
public int key;
public int val;
public DoubleNode last;
public DoubleNode next;
public DoubleNode(int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
class DoubleList {
// 只定义头尾指针
// <头指针> 指向操作时间 <最早> 的节点
// <尾指针> 指向操作时间 <最晚> 的节点
private DoubleNode head;
private DoubleNode tail;
public DoubleList() {
head = null;
tail = null;
}
public void addNode(DoubleNode newNode) {
if (newNode == null) {
return;
}
// 添加的节点是第一个节点
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
} else {
// 挂接新节点,同时调整两个指针
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.last = tail;
// 尾节点来到新的尾巴,继续挂接下一个节点
tail = newNode;
}
}
// 删除操作时间最早的节点,即删除头节点
public DoubleNode removeHead() {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
DoubleNode ans = head;
// 只有一个节点
if (head == tail) {
head = null;
tail = null;
} else {
// head 来到头节点的下一个节点
head = ans.next;
// 删除头节点,处理两个指针
ans.next = null;
head.last = null;
}
return ans;
}
// 对元素操作后,需要调整时序
public void moveNodeToTail(DoubleNode node) {
// 只有一个节点,无需调整
if (tail == node) {
return;
}
// 如果头节点,调整头指针
if (head == node) {
head = node.next;
head.last = null;
} else {
// 节点是中间节点,将该节点从链表中分离
// 调整 lastNode 的 next 指针
node.last.next = node.next;
// 调整 nextNode 的 last 指针
node.next.last = node.last;
}
// 调整指针,挂接节点
tail.next = node;
node.last = tail;
node.next = node;
tail = node;
}
}
private HashMap<Integer, DoubleNode> keyNodeMap;
private DoubleList nodeList;
private final int capacity;
public LRUCache(int n) {
keyNodeMap = new HashMap<>();
nodeList = new DoubleList();
capacity = n;
}
public int get(int key) {
if (keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
DoubleNode ans = keyNodeMap.get(key);
nodeList.moveNodeToTail(ans);
return ans.val;
}
// 不存在返回 -1
return -1;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
// 如果 key 存在就更新 value,否则就新增 key
if (keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
DoubleNode node = keyNodeMap.get(key);
node.val = value;
nodeList.moveNodeToTail(node);
} else {
// 新增之前先判断是否满容量
// 满容量的情况下要新增,移除头节点
if (keyNodeMap.size() == capacity) {
// nodeList.removeHead() 返回头节点
keyNodeMap.remove(nodeList.removeHead().key);
}
DoubleNode newNode = new DoubleNode(key, value);
keyNodeMap.put(key, newNode);
nodeList.addNode(newNode);
}
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/O(1) 增删和获取随机元素-1
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/insert-delete-getrandom-o1/
思路分析
采用 map 结构,key 存储元素值,vval 存储元素下标
定义一个动态数组,存储元素
remove 删除元素,如果在 random 的时候恰好随机到被删除的元素,这就会产生问题
如果 remove 元素,拿动态数组的最后一个元素填补空缺,同时更新 map 中元素对应的下标
代码实现
java
class RandomizedSet {
public HashMap<Integer, Integer> map;
public ArrayList<Integer> arr;
public RandomizedSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
arr = new ArrayList<>();
}
public boolean insert(int val) {
if (map.containsKey(val)) {
return false;
}
map.put(val, arr.size());
arr.add(val);
return true;
}
public boolean remove(int val) {
if (!map.containsKey(val)) {
return false;
}
// 删除一个数产生的空缺用最后一个数填补
int valIndex = map.get(val);
int endValue = arr.get(arr.size() - 1);
map.put(endValue, valIndex);
arr.set(valIndex, endValue);
map.remove(val);
arr.remove(arr.size() - 1);
return true;
}
public int getRandom() {
return arr.get((int) (Math.random() * arr.size()));
}
}
/**
* Your RandomizedSet object will be instantiated and called as such:
* RandomizedSet obj = new RandomizedSet();
* boolean param_1 = obj.insert(val);
* boolean param_2 = obj.remove(val);
* int param_3 = obj.getRandom();
*/O(1) 增删和获取随机元素-2
💡 Tip
区别于上题,本题允许有重复元素,getRandom()从当前的多个元素集合中返回一个随机元素。每个元素被返回的概率与集合中包含的相同值的数量线性相关
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/insert-delete-getrandom-o1-duplicates-allowed/
思路分析
跟上题思路类似,由于允许重复元素存在,map 中的 value 变为 set 结构,存储多个重复元素的下标
代码实现
java
class RandomizedCollection {
private HashMap<Integer, HashSet<Integer>> map;
private ArrayList<Integer> arr;
public RandomizedCollection() {
map = new HashMap<>();
arr = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 第一次加入返回 true,否则返回 false
public boolean insert(int val) {
arr.add(val);
HashSet<Integer> set = map.getOrDefault(val, new HashSet<Integer>());
// 记录元素的下标
set.add(arr.size() - 1);
map.put(val, set);
return set.size() == 1;
}
public boolean remove(int val) {
if (!map.containsKey(val)) {
return false;
}
HashSet<Integer> valIndexSet = map.get(val);
int valAnyIndex = valIndexSet.iterator().next();
int endValue = arr.get(arr.size() - 1);
// 如果删除的是最后一个元素,直接删除,无需填补
if (val == endValue) {
valIndexSet.remove(arr.size() - 1);
} else {
// 用最后一个数去填补删除元素产生的空缺
HashSet<Integer> endValueSet = map.get(endValue);
endValueSet.add(valAnyIndex);
arr.set(valAnyIndex, endValue);
endValueSet.remove(arr.size() - 1);
valIndexSet.remove(valAnyIndex);
}
arr.remove(arr.size() - 1);
if (valIndexSet.isEmpty()) {
map.remove(val);
}
return true;
}
public int getRandom() {
return arr.get((int) (Math.random() * arr.size()));
}
}
/**
* Your RandomizedCollection object will be instantiated and called as such:
* RandomizedCollection obj = new RandomizedCollection();
* boolean param_1 = obj.insert(val);
* boolean param_2 = obj.remove(val);
* int param_3 = obj.getRandom();
*/获取数据流的中位数
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-median-from-data-stream/
思路分析
求中位数的前提是有序
可以利用有序的特点,运用两个堆实现,维护中间值
左边较小的部分放在大顶堆中,右边较大的部分放在小顶堆中,那两个堆的堆顶元素就是中间值
只要两个堆的大小差值不大于 2,就无需调整堆
如果总元素个数是奇数,则中位数就是大顶堆的堆顶元素
如果总元素个数是偶数,则中位数是两个堆的堆顶元素的平均值
代码实现
java
class MedianFinder {
// 较大的元素放在小根堆
private PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap;
// 较小的元素放在大根堆
private PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap;
public MedianFinder() {
minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a - b);
maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a);
}
public void addNum(int num) {
if (maxHeap.isEmpty() || num <= maxHeap.peek()) {
maxHeap.add(num);
} else {
minHeap.add(num);
}
balance();
}
public double findMedian() {
// 元素个数是偶数个
if (maxHeap.size() == minHeap.size()) {
return (double) (maxHeap.peek() + minHeap.peek()) / 2;
} else {
// 元素个数是奇数个
return maxHeap.size() > minHeap.size() ? maxHeap.peek() : minHeap.peek();
}
}
public void balance() {
if (Math.abs(maxHeap.size() - minHeap.size()) == 2) {
if (maxHeap.size() > minHeap.size()) {
// 大根堆弹出一个进小根堆
minHeap.add(maxHeap.poll());
} else {
// 小根堆弹出一个进大根堆
maxHeap.add(minHeap.poll());
}
}
}
}
/**
* Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MedianFinder obj = new MedianFinder();
* obj.addNum(num);
* double param_2 = obj.findMedian();
*/最大频率栈
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-frequency-stack
思路分析

代码实现
java
class FreqStack {
// 出现的最大次数
private int topTimes;
// 每层节点
private HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> cntValues = new HashMap<>();
// 每一个数出现了几次(词频表)
private HashMap<Integer, Integer> valueTimes = new HashMap<>();
public void push(int val) {
// 更新自己的词频
valueTimes.put(val, valueTimes.getOrDefault(val, 0) + 1);
// 当前元素的最大词频,后续可能会更新
int curTopTimes = valueTimes.get(val);
// 如果当前词频对应的层么米有链表,建出来
if (!cntValues.containsKey(curTopTimes)) {
cntValues.put(curTopTimes, new ArrayList<>());
}
// 拿到当前词频对应层的链表,添加元素
ArrayList<Integer> curTimeValues = cntValues.get(curTopTimes);
curTimeValues.add(val);
// 更新最大词频
topTimes = Math.max(topTimes, curTopTimes);
}
public int pop() {
// 弹出词频最大的元素
ArrayList<Integer> topTimeValues = cntValues.get(topTimes);
// 同一层链表,从右往左移除元素
// 返回移除的数字,目的是后续更新词频表
int ans = topTimeValues.remove(topTimeValues.size() - 1);
// 如果元素没了,清除当前层的链表
if (topTimeValues.size() == 0) {
cntValues.remove(topTimes);
topTimes--;
}
// 更新移除元素对应的词频
int times = valueTimes.get(ans);
// 要移除的数字只剩下依次,再移除就没了
if (times == 1) {
valueTimes.remove(ans);
} else {
valueTimes.put(ans, times - 1);
}
return ans;
}
}
/**
* Your FreqStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* FreqStack obj = new FreqStack();
* obj.push(val);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
*/全 O(1)的数据结构
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/all-oone-data-structure
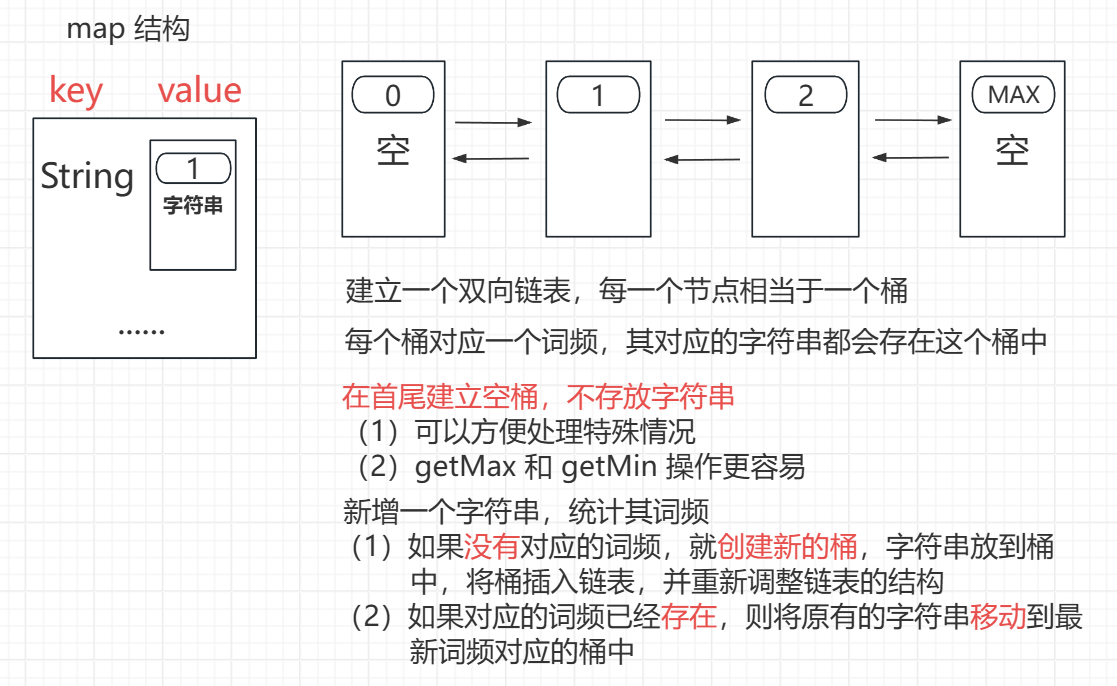
思路分析
代码实现
java
class AllOne {
// 定义双向链表节点(桶)
class Bucket {
// 词频
public int cnt;
// 该词频对应的字符串
public HashSet<String> set;
public Bucket last;
public Bucket next;
public Bucket(String s, int n) {
set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(s);
cnt = n;
}
}
// 在 cur 桶(节点)的后面插入 pos 桶(节点)
public void insert(Bucket cur, Bucket pos) {
// 先处理后面,再处理前面
pos.next = cur.next;
cur.next.last = pos;
cur.next = pos;
pos.last = cur;
}
// 移除 cur 桶(节点)
public void remove(Bucket cur) {
cur.last.next = cur.next;
cur.next.last = cur.last;
}
// 头桶指针
Bucket head;
// 尾桶指针
Bucket tail;
HashMap<String, Bucket> map;
// 初始化,建立首尾两个桶,不存储字符串
public AllOne() {
head = new Bucket("", 0);
tail = new Bucket("", Integer.MAX_VALUE);
head.next = tail;
tail.last = head;
map = new HashMap<>();
}
// 整体思路
// 如果链表 有 对应的词频,就以最新的词频为准,移动字符串
// 如果链表中 没有 对应的词频,就创建新的桶,加入双向链表
public void inc(String key) {
// 字符串第一次进来,放到词频为 1 的桶中
if (!map.containsKey(key)) {
// 词频为 1 的桶存在,直接放入
if (head.next.cnt == 1) {
map.put(key, head.next);
head.next.set.add(key);
} else {
// 词频为 1 的桶不存在,创建桶并插入到链表中
Bucket bucket = new Bucket(key, 1);
map.put(key, bucket);
// 在 head 桶的后面插入 bucket 桶
insert(head, bucket);
}
} else {
Bucket bucket = map.get(key);
// 需要插入 key,看是否存在词频为 bucket.cnt + 1 的桶
if (bucket.next.cnt == bucket.cnt + 1) {
map.put(key, bucket.next);
bucket.next.set.add(key);
} else {
Bucket newBucket = new Bucket(key, bucket.cnt + 1);
map.put(key, newBucket);
insert(bucket, newBucket);
}
// 字符串移动了到了新的桶,更新原来的桶
bucket.set.remove(key);
// 如果桶空了,把桶移除
if (bucket.set.isEmpty()) {
// 前后节点重连,移除 bucket 桶
remove(bucket);
}
}
}
public void dec(String key) {
Bucket bucket = map.get(key);
// 字符串的词频只有 1,删除就没了
if (bucket.cnt == 1) {
map.remove(key);
} else {
// 有对应词频的桶就移动字符串,否则新建
if (bucket.last.cnt == bucket.cnt - 1) {
map.put(key, bucket.last);
bucket.last.set.add(key);
} else {
Bucket newBucket = new Bucket(key, bucket.cnt - 1);
map.put(key, newBucket);
insert(bucket.last, newBucket);
}
}
// 字符串移动了到了新的桶,更新原来的桶
bucket.set.remove(key);
// 如果桶空了,把桶移除
if (bucket.set.isEmpty()) {
remove(bucket);
}
}
public String getMaxKey() {
return tail.last.set.iterator().next();
}
public String getMinKey() {
return head.next.set.iterator().next();
}
}
/**
* Your AllOne object will be instantiated and called as such:
* AllOne obj = new AllOne();
* obj.inc(key);
* obj.dec(key);
* String param_3 = obj.getMaxKey();
* String param_4 = obj.getMinKey();
*/