队列与栈互相实现
栈实现队列
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/
思路分析
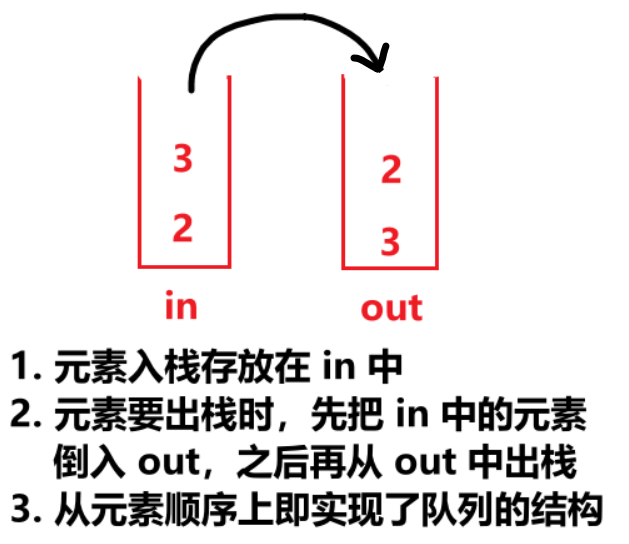
定义两个栈,inStack,outStack,入栈元素存放在 inStack,出栈元素从 outStack 弹出
⚠️ 两大注意点
(1)out 空了,才能倒数据
(2)如果倒数据,in 必须倒完
代码实现
java
class MyQueue {
public Stack<Integer> in;
public Stack<Integer> out;
public MyQueue() {
in = new Stack<Integer>();
out = new Stack<Integer>();
}
// 倒数据
// 从 in 栈,把数据倒入 out 栈
// (1) out 空了,才能倒数据
// (2)如果倒数据,in 必须倒完
private void inToOut() {
if (out.empty()) {
while (!in.empty()) {
out.push(in.pop());
}
}
}
public void push(int x) {
in.push(x);
// 如果不能倒数据就啥也不做
inToOut();
}
public int pop() {
inToOut();
return out.pop();
}
public int peek() {
inToOut();
return out.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return in.isEmpty() && out.isEmpty();
}
}队列实现栈
题目链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/
思路分析
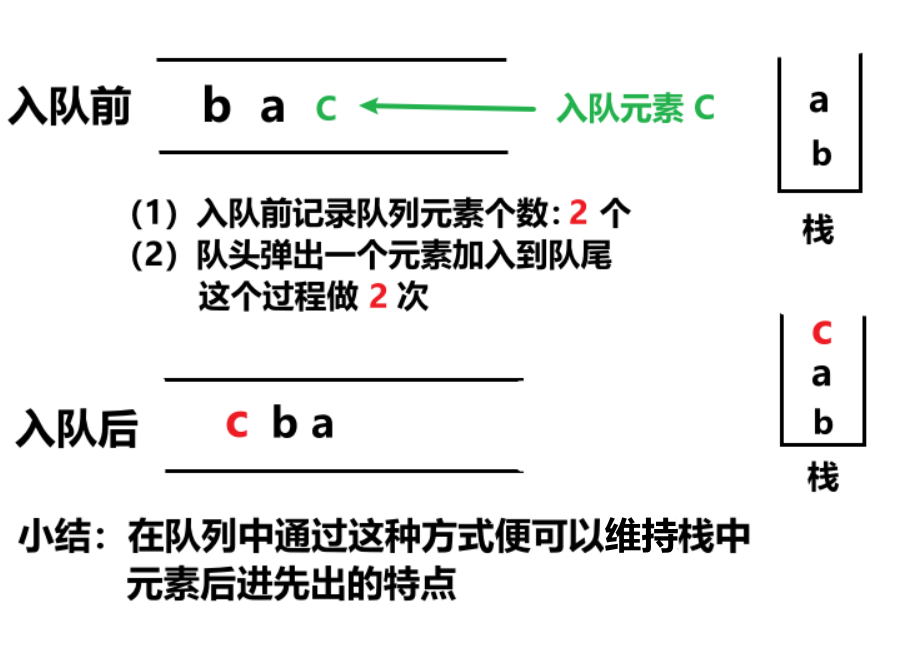
每加入一个元素,就记录当前队列中的元素个数
之后从队头弹出一个元素加入到队列的末尾,这个过程循环 queue.size() 次
这样就可以在队列结构的情况下保证元素是后进先出的
代码实现
java
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue;
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
// O(n)
public void push(int x) {
int n = queue.size();
queue.offer(x);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
queue.offer(queue.poll());
}
}
public int pop() {
return queue.poll();
}
public int top() {
return queue.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}