前缀树原理与代码详解
基本介绍
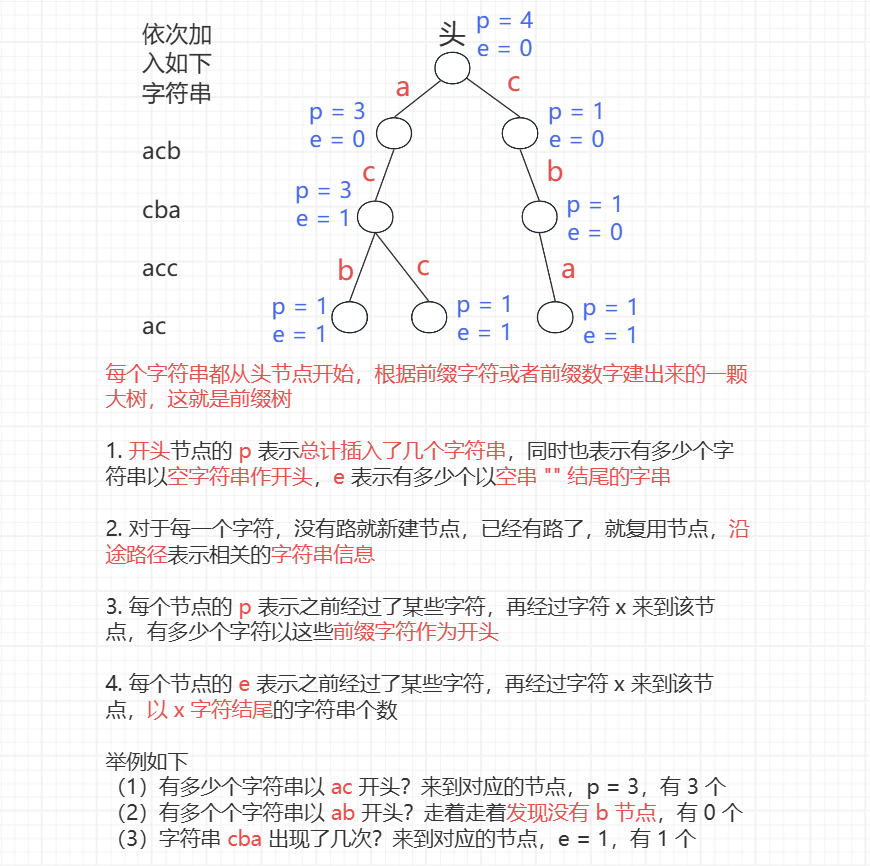
前缀树又叫字典树,英文名 trie
每个样本都从头节点开始根据前缀字符或者前缀数 建出来的一棵大树,就是前缀树
没有路就新建节点,已经有路了,就复用节点
前缀树的使用场景:需要根据前缀信息来查询的场景
前缀树的优点:根据前缀信息选择树上的分支,可以节省大量的时间
前缀树的缺点:比较浪费空间,和总字符数量有关,字符的种类有关
前缀树的定制:pass、end 等信息
结构图解
类描述实现(不推荐)
题目链接
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/7f8a8553ddbf4eaab749ec988726702b
数组实现
java
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static int m, op;
public static String[] splits;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String line = null;
Trie trie = new Trie();
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
m = Integer.valueOf(line);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
splits = in.readLine().split(" ");
op = Integer.valueOf(splits[0]);
if (op == 1) {
trie.insert(splits[1]);
} else if (op == 2) {
trie.delete(splits[1]);
} else if (op == 3) {
out.println(trie.search(splits[1]) > 0 ? "YES" : "NO");
} else if (op == 4) {
out.println(trie.prefixNumber(splits[1]));
}
}
}
out.flush();
in.close();
out.close();
}
}
class Trie {
// 定义头节点指针
private TrieNode root;
// 头节点
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// 插入字符串,构建前缀树
public void insert(String word) {
// 定义节点遍历指针
TrieNode node = root;
node.pass++;
// 遍历所有每一个字符
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
// path 的值是下标索引,每一个下标对应一条路
// 即这一句表示得到每一个字符对应走向那条路
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
// 如果没有走向这个字符的路,就创建出来
if (node.nexts[path] == null) {
node.nexts[path] = new TrieNode();
}
// 如果有,就更新节点信息,同时移动遍历指针
node = node.nexts[path];
node.pass++;
}
// 遍历完了,更新节点的 end 值
node.end++;
}
// 查询前缀树里有多少字符串以 pre 做前缀
public int prefixNumber(String pre) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (int i = 0, path; i < pre.length(); i++) {
path = pre.charAt(i) - 'a';
// 没有到该节点的路,当前没有这个前缀,返回 0
if (node.nexts[path] == null) {
return 0;
}
node = node.nexts[path];
}
return node.pass;
}
// 查询前缀树中字符串 str 的个数
public int search(String word) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (node.nexts[path] == null) {
return 0;
}
node = node.nexts[path];
}
return node.end;
}
// 在前缀树中删除某个字符串
// 如果之前 str 插入过前缀树,那么此时删掉一次
// 如果之前 str 没有插入过前缀树,那么什么也不做
public void delete(String word) {
if (search(word) > 0) {
TrieNode node = root;
node.pass--;
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
// 如果为 0,后续的所有节点都不可能到达,置空
// 剩余的节点会有 JVM 回收,无需手动释放
if (--node.nexts[path].pass == 0) {
node.nexts[path] = null;
return;
}
node = node.nexts[path];
}
// 还有一种可能就是后续的节点还有用,只是以该节点
// 为结尾的字符串删除了,更新节点的 end 值即可
node.end--;
}
}
class TrieNode {
// 记录前缀信息
public int pass;
public int end;
// 存储所有可能到达的字符
public TrieNode[] nexts;
public TrieNode() {
pass = 0;
end = 0;
// 假设只有 26 个小写字母
// 根据实际情况改变大小
nexts = new TrieNode[26];
}
}
}哈希表实现
如果字符的种类很多,那就会有非常多的分叉,此时可以用哈希表来存储这些分叉
key 是路的数值,vlaue 是节点的地址
需要判断有没有某一条路,直接查表即可
java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static int m, op;
public static String[] splits;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String line = null;
Trie trie = new Trie();
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
m = Integer.valueOf(line);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
splits = in.readLine().split(" ");
op = Integer.valueOf(splits[0]);
if (op == 1) {
trie.insert(splits[1]);
} else if (op == 2) {
trie.delete(splits[1]);
} else if (op == 3) {
out.println(trie.search(splits[1]) > 0 ? "YES" : "NO");
} else if (op == 4) {
out.println(trie.prefixNumber(splits[1]));
}
}
}
out.flush();
in.close();
out.close();
}
}
class Trie {
// 定义头节点指针
private TrieNode root;
// 头节点
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// 插入字符串,构建前缀树
public void insert(String word) {
// 定义节点遍历指针
TrieNode node = root;
node.pass++;
// 遍历所有每一个字符
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
// path 的值是下标索引,每一个下标对应一条路
// 即这一句表示得到每一个字符对应走向那条路
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
// 如果没有走向这个字符的路,就创建出来
if (!node.nexts.containsKey(path)) {
node.nexts.put(path, new TrieNode());
}
// 如果有,就更新节点信息,同时移动遍历指针
node = node.nexts.get(path);
node.pass++;
}
// 遍历完了,更新节点的 end 值
node.end++;
}
// 查询前缀树里有多少字符串以 pre 做前缀
public int prefixNumber(String pre) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (int i = 0, path; i < pre.length(); i++) {
path = pre.charAt(i) - 'a';
// 没有到该节点的路,当前没有这个前缀,返回 0
if (!node.nexts.containsKey(path)) {
return 0;
}
node = node.nexts.get(path);
}
return node.pass;
}
// 查询前缀树中字符串 str 的个数
public int search(String word) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (!node.nexts.containsKey(path)) {
return 0;
}
node = node.nexts.get(path);
}
return node.end;
}
// 在前缀树中删除某个字符串
// 如果之前 str 插入过前缀树,那么此时删掉一次
// 如果之前 str 没有插入过前缀树,那么什么也不做
public void delete(String word) {
if (search(word) > 0) {
TrieNode node = root;
TrieNode next;
node.pass--;
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
next = node.nexts.get(path);
// 如果为 0,后续的所有节点都不可能到达,置空
// 剩余的节点会有 JVM 回收,无需手动释放
if (--next.pass == 0) {
node.nexts.remove(path);
return;
}
node = next;
}
// 还有一种可能就是后续的节点还有用,只是以该节点
// 为结尾的字符串删除了,更新节点的 end 值即可
node.end--;
}
}
class TrieNode {
// 记录前缀信息
public int pass;
public int end;
// 用哈希表存储所有可能到达的字符
public HashMap<Integer, TrieNode> nexts;
public TrieNode() {
pass = 0;
end = 0;
// 假设只有 26 个小写字母
// 根据实际情况改变大小
nexts = new HashMap<>();
}
}
}缺陷分析
类实现是基于动态数组实现的,每次都会申请新的内存空间
在 OJ 判题系统中,内存的计算是逐层累加的,每跑完一次测试用例,动态申请的空间销毁,但是会累加计算内存,再跑下一组测试用例继续计算
最终的空间使用的结果都算累加的这个结果,累加过程中可能会导致内存超过限制
静态数组实现(推荐)
题目链接
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/7f8a8553ddbf4eaab749ec988726702b
思路分析
通过节点编号来表示节点,而不是真的创建一个节点,空间使用更优
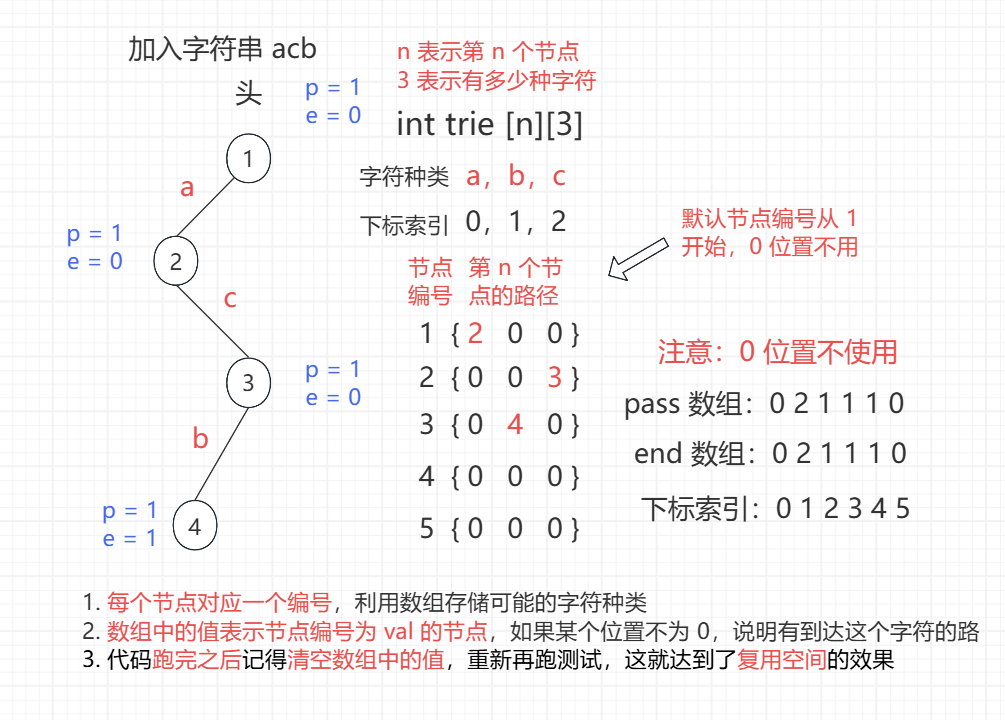
Main 中实现写法
java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
// 如果将来增加了数据量,就改大这个值
public static int MAXN = 150001;
public static int[][] tree = new int[MAXN][26];
public static int[] end = new int[MAXN];
public static int[] pass = new int[MAXN];
public static int cnt;
public static void build() {
// 头节点的编号为 1
cnt = 1;
}
public static void insert(String word) {
// 头节点的编号是 1
int cur = 1;
pass[cur]++;
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
// 没有到达该节点的路,建立出来
if (tree[cur][path] == 0) {
tree[cur][path] = ++cnt;
}
cur = tree[cur][path];
pass[cur]++;
}
end[cur]++;
}
public static int prefixNumber(String pre) {
int cur = 1;
for (int i = 0, path; i < pre.length(); i++) {
path = pre.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (tree[cur][path] == 0) {
return 0;
}
cur = tree[cur][path];
}
return pass[cur];
}
public static int search(String word) {
int cur = 1;
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (tree[cur][path] == 0) {
return 0;
}
cur = tree[cur][path];
}
return end[cur];
}
public static void delete(String word) {
if (search(word) > 0) {
int cur = 1;
pass[cur]--;
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
// 后续的节点都无法到达,直接置为 0
if (--pass[tree[cur][path]] == 0) {
tree[cur][path] = 0;
return;
}
cur = tree[cur][path];
}
end[cur]--;
}
}
// 因为要跑多组测试用例,而使用的是静态空间
// 为了避免脏数据污染,所以这里要清空数据
public static void clear() {
// 并不需要全部清空,cnt 代表使用了多少空间
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
Arrays.fill(tree[i], 0);
end[i] = 0;
pass[i] = 0;
}
}
public static int m, op;
public static String[] splits;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
build();
m = Integer.valueOf(line);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
splits = in.readLine().split(" ");
op = Integer.valueOf(splits[0]);
if (op == 1) {
insert(splits[1]);
} else if (op == 2) {
delete(splits[1]);
} else if (op == 3) {
out.println(search(splits[1]) > 0 ? "YES" : "NO");
} else if (op == 4) {
out.println(prefixNumber(splits[1]));
}
}
clear();
}
out.flush();
in.close();
out.close();
}
}类封装写法
java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static int m, op;
public static String[] splits;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String line = null;
Trie trie = new Trie();
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
trie.build();
m = Integer.valueOf(line);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
splits = in.readLine().split(" ");
op = Integer.valueOf(splits[0]);
if (op == 1) {
trie.insert(splits[1]);
} else if (op == 2) {
trie.delete(splits[1]);
} else if (op == 3) {
out.println(trie.search(splits[1]) > 0 ? "YES" : "NO");
} else if (op == 4) {
out.println(trie.prefixNumber(splits[1]));
}
}
trie.clear();
}
out.flush();
in.close();
out.close();
}
}
class Trie {
// 如果将来增加了数据量,就改大这个值
public static int MAXN = 150001;
public static int[][] tree = new int[MAXN][26];
public static int[] end = new int[MAXN];
public static int[] pass = new int[MAXN];
public static int cnt;
public void build() {
cnt = 1;
}
public void insert(String word) {
int cur = 1;
pass[cur]++;
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (tree[cur][path] == 0) {
tree[cur][path] = ++cnt;
}
cur = tree[cur][path];
pass[cur]++;
}
end[cur]++;
}
public int search(String word) {
int cur = 1;
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (tree[cur][path] == 0) {
return 0;
}
cur = tree[cur][path];
}
return end[cur];
}
public int prefixNumber(String pre) {
int cur = 1;
for (int i = 0, path; i < pre.length(); i++) {
path = pre.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (tree[cur][path] == 0) {
return 0;
}
cur = tree[cur][path];
}
return pass[cur];
}
public void delete(String word) {
if (search(word) > 0) {
int cur = 1;
// 下面这一行代码,讲课的时候没加
// 本题不会用到pass[1]的信息,所以加不加都可以,不过正确的写法是加上
pass[cur]--;
for (int i = 0, path; i < word.length(); i++) {
path = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (--pass[tree[cur][path]] == 0) {
tree[cur][path] = 0;
return;
}
cur = tree[cur][path];
}
end[cur]--;
}
}
public void clear() {
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
Arrays.fill(tree[i], 0);
end[i] = 0;
pass[i] = 0;
}
}
}缺陷分析
Java 字符串理论上最大长度是 Integer.MAX_VALUE(约 21 亿),但在 class 文件格式中,常量池索引是 16 位,所以某些结构(如方法参数数量、单个字符串常量)编译时常量不能超过 65535 字节
如果需要表示的字符种类巨大,即如果路的可能性范围较大,静态数组就无法实现了,可以用每一位的信息建树,目标值由每一位的信息构建,这将再下节课前缀树的题目里展示
