Day 46
110.字符串接龙
经过上面的练习,大家可能会感觉 广搜不过如此,都刷出自信了,本题让大家初步感受一下,广搜难不在广搜本身,而是如何应用广搜。
题目链接:https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1183
文章讲解:https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/0110.字符串接龙.html
视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1QEEizDEC4
思路分析
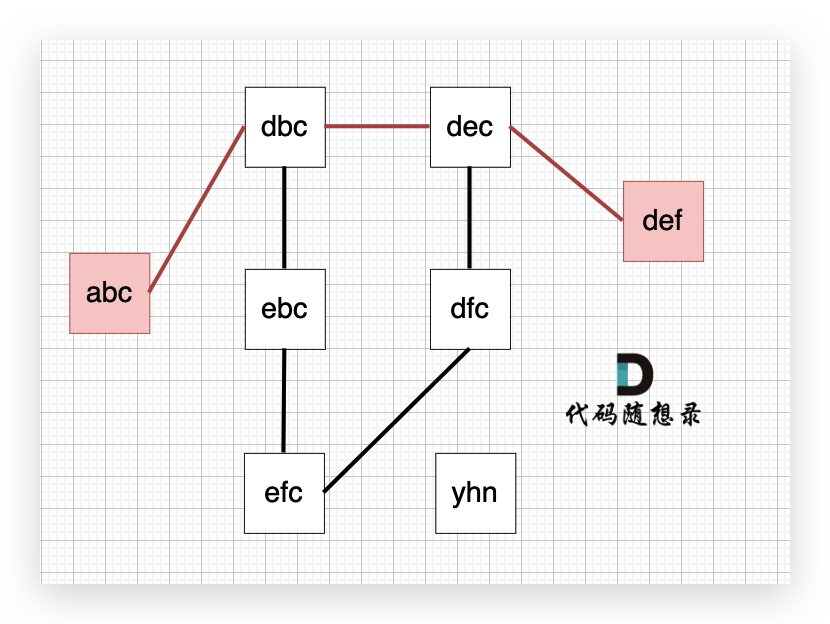
1、图中的线是如何连在一起的
在搜索的过程中,我们可以枚举,用 26 个字母替换当前字符串的每一个字符,在看替换后是否在 strList 里出现过,就可以判断两个字符串是否是连接的
2、起点和终点的最短路径长度
(1)首先题目中并没有给出点与点之间的连线,而是要我们自己去连,条件是字符只能差一个
(2)所以判断点与点之间的关系,需要判断是不是差一个字符,如果差一个字符,那就是有连接
(3)然后就是求起点和终点的最短路径长度,在无权图中,求最短路,用深搜或者广搜就行,没必要用最短路算法
在无权图中,用广搜求最短路最为合适,广搜只要搜到了终点,那么一定是最短的路径。因为广搜就是以起点中心向四周扩散的搜索
3. 本题如果用深搜,会比较麻烦,要在到达终点的不同路径中选则一条最短路,而广搜只要达到终点,一定是最短路
4. 另外需要有一个注意点
本题是一个无向图,需要用标记位,标记着节点是否走过,否则就会死循环!使用 set 来检查字符串是否出现在字符串集合里更快一些
题解
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static Set<String> wordList = new HashSet<>();
static Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
String beginStr = sc.next();
String endStr = sc.next();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
wordList.add(sc.next());
}
map.put(beginStr, 1);
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(beginStr);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
String word = q.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char[] arr = word.toCharArray();
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
arr[i] = c;
String word2 = new String(arr);
// 到达终点
if (word2.equals(endStr)) {
// 到达当前节点的路径 = 到达上一个节点的路径 + 1
System.out.println(map.get(word) + 1);
return;
}
// 替换后的新字符串如果是字典序中的字符串,并且没有被访问过,则加入队列
if (wordList.contains(word2) && !map.containsKey(word2)) {
// 到达当前节点的路径 = 到达上一个节点的路径 + 1
map.put(word2, map.get(word) + 1);
q.offer(word2);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(0);
}
}105.有向图的完全可达性
深搜有细节,同样是深搜两种写法的区别,以及什么时候需要回溯操作呢?
题目链接:https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1177
文章讲解:https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/0105.有向图的完全可达性.html
视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1QRJ6ziEvJ
思路分析
使用 dfs 遍历所有节点并作标记,若最后有节点未标记,则说明无法到达所有节点
题解
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
// 邻接表
public static List<List<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList<>();
public static void dfs(boolean[] visited, int key) {
// 首先处理当前节点
visited[x] = true;
List<Integer> list = adjList.get(x);
for (Integer val : list) {
if (!visited[val]) {
dfs(val, visited);
}
}
}
public static void bfs(boolean[] visited, int key) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.add(key);
// 只要加入队列就标记为访问过
visited[key] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int curKey = queue.poll();
List<Integer> list = adjList.get(curKey);
for (int nextKey : list) {
if (!visited[nextKey]) {
queue.add(nextKey);
visited[nextKey] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 顶点
int vertices_num = sc.nextInt();
// 边
int line_num = sc.nextInt();
// 初始化邻接表(实际使用时节点编号和下标索引对应)
for (int i = 0; i <= vertices_num; i++) {
adjList.add(new LinkedList<>());
}
// 输入 k 条边
for (int i = 0; i < line_num; i++) {
int s = sc.nextInt();
int t = sc.nextInt();
// 节点编号和索引下标对应
adjList.get(s).add(t);
}
// n 个节点,节点编号和索引下标对应
boolean[] visited = new boolean[vertices_num + 1];
dfs(visited, 1);
// bfs(visited, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= vertices_num; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
System.out.println(-1);
// 这里要写 return,表示结束整个函数
return;
}
}
System.out.println(1);
}
}106.岛屿的周长
简单题,避免大家惯性思维,建议大家先独立做题。
题目链接:https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1178
文章讲解:https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/0106.岛屿的周长.html
视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV13fjczSEyV
思路分析
无需使用深搜或广搜,遍历一遍地图,判断当前节点周围的情况,如果是边界或者水,周长加一
题解
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int[][] dirs = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
// 统计每单个 1 的周长
static int count;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 接收输入
int M = sc.nextInt();
int N = sc.nextInt();
int[][] grid = new int[M][N];
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
// 如果是陆地,就检查四周的情况
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int nx = i + dir[0];
int ny = j + dir[1];
// 四周遇到边界或者水,周长加一
if (nx < 0 || nx >= grid.length || ny < 0 || ny >= grid[0].length
|| grid[nx][ny] == 0) {
count++;
}
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}