Day 52
今天大家会感受到 Bellman_ford 算法系列在不同场景下的应用。
建议依然是:一刷的时候,能理解 原理,知道 Bellman_ford 解决不同场景的问题 ,照着代码随想录能抄下来代码就好,就算达标。
二刷的时候自己尝试独立去写,三刷的时候 才能有一定深度理解各个最短路算法。
Bellman_ford 队列优化算法(又名 SPFA)
题目链接:https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1152
文章讲解:https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/0094.城市间货物运输I-SPFA.html
视频讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1YehwzdEVT
思路分析
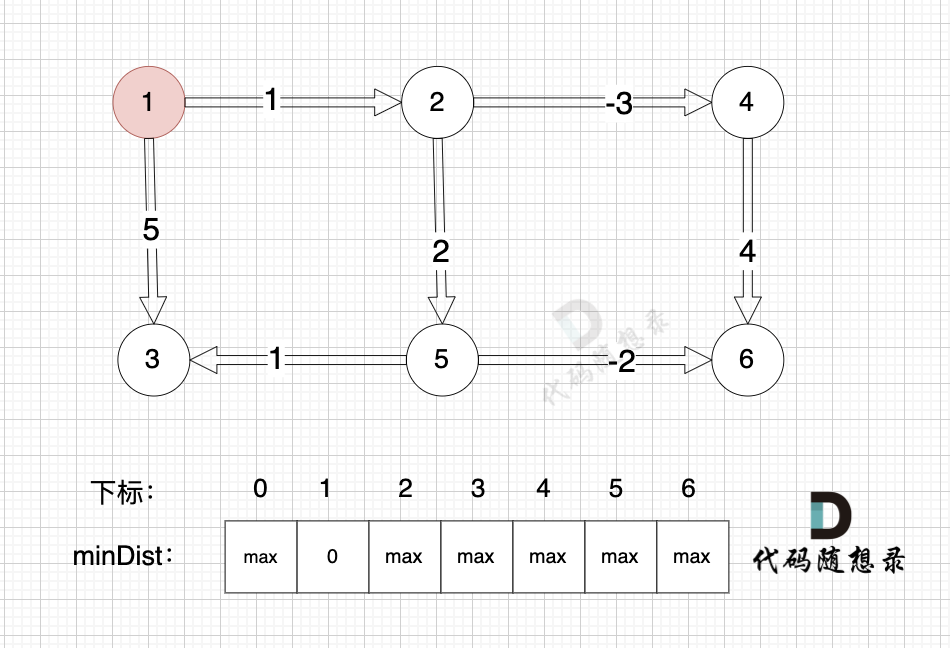
问题分析
本图中,对所有边进行松弛,真正有效的松弛,只有松弛 边(节点 1->节点 2) 和 边(节点 1->节点 3)
而松弛 边(节点 4->节点 6) ,边(节点 5->节点 3)等等 都是无效的操作,因为 节点 4 和 节点 5 都是没有被计算过的节点,所以 Bellman_ford 算法 每次都是对所有边进行松弛,其实是多做了一些无用功
松弛优化思路
只需要对上一次松弛的时候更新过的节点作为出发节点所连接的边进行松弛就够了
队列实现
将当前节点入队,取出队头节点,把队头节点相连的节点加入队列,同时对边进行松弛
题解
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Edge {
int from;
int to;
int val;
public Edge(int from, int to, int val) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.val = val;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int m = scanner.nextInt();
List<List<Edge>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
// 节点编号从 1 开始
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// 邻接表存储(使用二维数组实现)
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int from = scanner.nextInt();
int to = scanner.nextInt();
int val = scanner.nextInt();
graph.get(from).add(new Edge(from, to, val));
}
int[] minDist = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(minDist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 起点到自身的最短距离为 0
minDist[1] = 0;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 节点 1 入队
queue.offer(1);
boolean[] isInQueue = new boolean[n + 1];
// SPFA
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int curNode = queue.poll();
isInQueue[curNode] = false;
// 遍历当前节点连接的节点
for (Edge edge : graph.get(curNode)) {
if (minDist[edge.from] + edge.val < minDist[edge.to]) {
minDist[edge.to] = minDist[edge.from] + edge.val;
// 避免重复加入队列,先做判断
if (!isInQueue[edge.to]) {
queue.offer(edge.to);
isInQueue[edge.to] = true;
}
}
}
}
if (minDist[n] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.println("unconnected");
} else {
System.out.println(minDist[n]);
}
}
}bellman_ford 之判断负权回路
题目链接:https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1153
文章讲解:https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/0095.城市间货物运输II.html
视频讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1EitczREi5
思路分析
问题分析
在没有负权回路的图中,松弛 n 次以上 ,结果不会有变化,但本题有 负权回路,如果松弛 n 次,结果就会有变化了,因为 有负权回路 就是可以无限最短路径(一直绕圈,就可以一直得到无限小的最短距离)
判断思路
松弛 n 次(原本只需松弛 n - 1 次),在第 n 次松弛后判断 minDist 数组是否变化,如果变化则说明存在负权回路
普通版本
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static class Edge {
int from;
int to;
int val;
public Edge(int from, int to, int val) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.val = val;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int m = scanner.nextInt();
List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int from = scanner.nextInt();
int to = scanner.nextInt();
int val = scanner.nextInt();
edges.add(new Edge(from, to, val));
}
int[] minDist = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(minDist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 源点到自身的距离为 0
minDist[1] = 0;
boolean flag = false;
// 松弛 n 次
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (Edge edge : edges) {
if (i < n) {
if (minDist[edge.from] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && minDist[edge.to] > minDist[edge.from] + edge.val) {
minDist[edge.to] = minDist[edge.from] + edge.val;
}
} else {
// 如果第 n 次 minDisst 数组发生变化,说明存在负权回路
if (minDist[edge.from] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && minDist[edge.to] > minDist[edge.from] + edge.val) {
flag = true;
}
}
}
}
if (flag) {
System.out.println("circle");
} else if (minDist[n] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.println("unconnected");
} else {
System.out.println(minDist[n]);
}
}
}队列优化版本
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Edge {
int from;
int to;
int val;
public Edge(int from, int to, int val) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.val = val;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
List<List<Edge>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
int val = sc.nextInt();
graph.get(from).add(new Edge(from, to, val));
}
int[] minDist = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(minDist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
minDist[1] = 0;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
int[] count = new int[n + 1];
count[1]++;
boolean[] isInQueue = new boolean[n + 1];
boolean flag = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int curNode = queue.poll();
isInQueue[curNode] = false;
for (Edge edge : graph.get(curNode)) {
if (minDist[edge.to] > minDist[edge.from] + edge.val) {
minDist[edge.to] = minDist[edge.from] + edge.val;
if (!isInQueue[edge.to]) {
queue.offer(edge.to);
isInQueue[edge.to] = true;
// 记录节点加入队列的次数
count[edge.to]++;
}
// n 个节点中,一个节点最多有 n - 1 个入度,即做多加入到队列 n - 1 次
if (count[edge.to] == n) {
flag = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
queue.poll();
}
break;
}
}
}
}
if (flag) {
System.out.println("circle");
} else if (minDist[n] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.println("unconnected");
} else {
System.out.println(minDist[n]);
}
}
}bellman_ford 之单源有限最短路
题目链接:https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1154
文章讲解:https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/0096.城市间货物运输III.html
视频讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1hQtdzAEBb
思路分析
本题加了限制:最多经过 k 个节点
即需要满足经过 k 个节点的条件下求最短路,且边的权值存在负数
核心突破点
(1)对所有边松弛一次,相当于计算起点到达与起点一条边相连的节点的最短距离
节点数量为 n,起点到终点,最多是 n-1 条边相连。 那么对所有边松弛 n-1 次 就一定能得到起点到达终点的最短距离
(2)本题是最多经过 k 个城市, 那么是 k + 1 条边相连的节点,对所有边松弛 k + 1 次即可
对所有边松弛一次,相当于计算起点到达与起点一条边相连的节点的最短距离,那么对所有边松弛 k + 1 次,就是求起点到达与起点 k + 1 条边相连的节点的最短距离
⚠️ 注意点
需要使用 minDist_copy 数组,minDist 一定要基于上次的 minDist 数值更新,不能使用本轮的 minDist 数值更新
bellman_ford 版本
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Edge {
int from;
int to;
int val;
public Edge(int from, int to, int val) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.val = val;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
List<Edge> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
int val = sc.nextInt();
graph.add(new Edge(from, to, val));
}
int src = sc.nextInt();
int dst = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
int[] minDist = new int[n + 1];
int[] minDistCopy;
Arrays.fill(minDist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
minDist[src] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k + 1; i++) {
// minDistCopy 是上一轮 minDist 数组的拷贝
minDistCopy = Arrays.copyOf(minDist, n + 1);
for (Edge edge : graph) {
int from = edge.from;
int to = edge.to;
int val = edge.val;
// 基于上一轮的 minDist 数组更新
if (minDistCopy[from] != Integer.MAX_VALUE
&& minDist[to] > minDistCopy[from] + val) {
minDist[to] = minDistCopy[from] + val;
}
}
}
if (minDist[dst] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.println("unreachable");
} else {
System.out.println(minDist[dst]);
}
}
}SPFA 版本
java
class Edge {
public int u; // 边的端点1
public int v; // 边的端点2
public int val; // 边的权值
public Edge() {
}
public Edge(int u, int v) {
this.u = u;
this.v = v;
this.val = 0;
}
public Edge(int u, int v, int val) {
this.u = u;
this.v = v;
this.val = val;
}
}
/**
* SPFA算法(版本3):处理含【负权回路】的有向图的最短路径问题
* bellman_ford(版本3) 的队列优化算法版本
* 限定起点、终点、至多途径k个节点
*/
public class SPFAForSSSP {
/**
* SPFA算法
*
* @param n 节点个数[1,n]
* @param graph 邻接表
* @param startIdx 开始节点(源点)
*/
public static int[] spfa(int n, List<List<Edge>> graph, int startIdx, int k) {
// 定义最大范围
int maxVal = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// minDist[i] 源点到节点i的最短距离
int[] minDist = new int[n + 1]; // 有效节点编号范围:[1,n]
Arrays.fill(minDist, maxVal); // 初始化为maxVal
minDist[startIdx] = 0; // 设置源点到源点的最短路径为0
// 定义queue记录每一次松弛更新的节点
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(startIdx); // 初始化:源点开始(queue和minDist的更新是同步的)
// SPFA算法核心:只对上一次松弛的时候更新过的节点关联的边进行松弛操作
while (k + 1 > 0 && !queue.isEmpty()) { // 限定松弛 k+1 次
int curSize = queue.size(); // 记录当前队列节点个数(上一次松弛更新的节点个数,用作分层统计)
while (curSize-- > 0) { //分层控制,限定本次松弛只针对上一次松弛更新的节点,不对新增的节点做处理
// 记录当前minDist状态,作为本次松弛的基础
int[] minDist_copy = Arrays.copyOfRange(minDist, 0, minDist.length);
// 取出节点
int cur = queue.poll();
// 获取cur节点关联的边,进行松弛操作
List<Edge> relateEdges = graph.get(cur);
for (Edge edge : relateEdges) {
int u = edge.u; // 与`cur`对照
int v = edge.v;
int weight = edge.val;
if (minDist_copy[u] + weight < minDist[v]) {
minDist[v] = minDist_copy[u] + weight; // 更新
// 队列同步更新(此处有一个针对队列的优化:就是如果已经存在于队列的元素不需要重复添加)
if (!queue.contains(v)) {
queue.offer(v); // 与minDist[i]同步更新,将本次更新的节点加入队列,用做下一个松弛的参考基础
}
}
}
}
// 当次松弛结束,次数-1
k--;
}
// 返回minDist
return minDist;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输入控制
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("1.输入N个节点、M条边(u v weight)");
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("2.输入M条边");
List<List<Edge>> graph = new ArrayList<>(); // 构建邻接表
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
while (m-- > 0) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
int weight = sc.nextInt();
graph.get(u).add(new Edge(u, v, weight));
}
System.out.println("3.输入src dst k(起点、终点、至多途径k个点)");
int src = sc.nextInt();
int dst = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
// 调用算法
int[] minDist = SPFAForSSSP.spfa(n, graph, src, k);
// 校验起点->终点
if (minDist[dst] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.println("unreachable");
} else {
System.out.println("最短路径:" + minDist[n]);
}
}
}