IO流
一、基本介绍
I/O 是 Input/Output 的缩写,I/O 技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理数据传输。如读 / 写文件,网络通讯等。
Java 程序中,对于数据的输入 / 输出操作以 “流 (stream)” 的方式进行。
java.io 包下提供了各种 “流” 类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过方法输入或输出数据
输入 input:读取外部数据(磁盘、光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中。
输出 output:将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘等存储设备中
二、流的分类
- 按操作数据单位不同分类
- 字节流(8 bit):二进制文件
- 字符流(按字符):文本文件
- 按数据流的流向分类
- 输入流
- 输出流
- 按流的角色的分类
- 节点流
- 处理流/包装流
| (抽象基类) | 字节流 | 字符流 |
|---|---|---|
| 输入流 | InputStream | Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream | Writer |
说明
- 以下四个类均为抽象类
- InputStream
- OutputStream
- Reader
- Writer
- Java 的 IO 流共涉及 40 多个类,实际上非常规则,都是从如上 4 个抽象基类派生的,由这四个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀(命名特点---> 记忆方法)
三、IO 流体系图
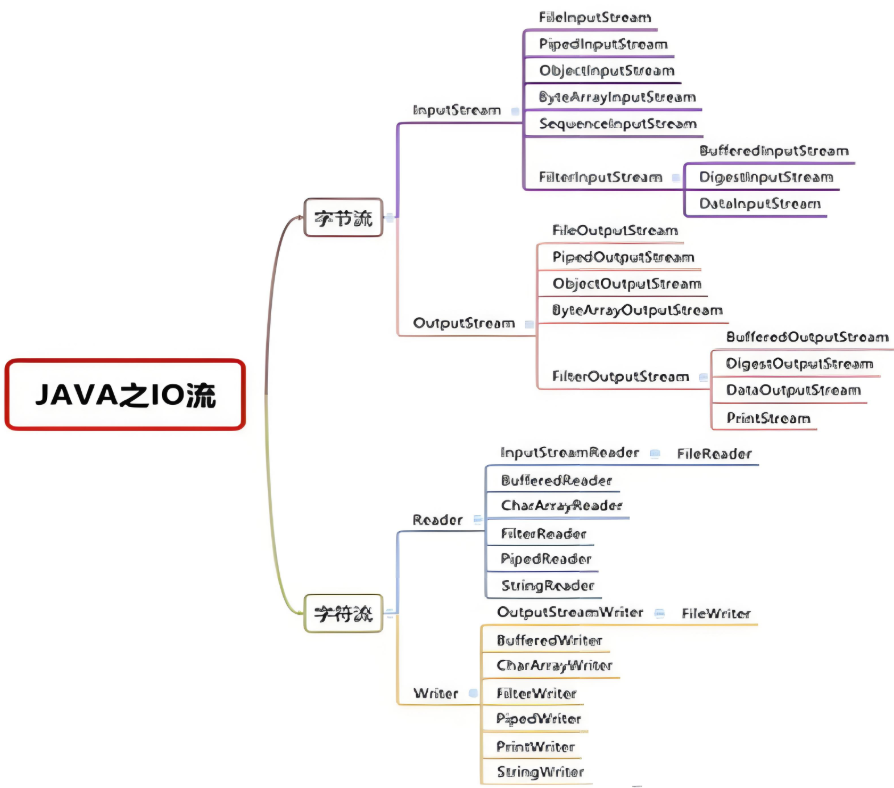
1. 字节流
InputStream
- FileInputStream
- PipedInputStream
- ObjectInputStream
- ByteArrayInputStream
- SequenceInputStream
- FilterInputStream
- BufferedInputStream
- DataInputStream
- DigestInputStream
OutputStream
- FileOutputStream
- PipedOutputStream
- ObjectOutputStream
- ByteArrayOutputStream
- FilterOutputStream
- BufferedOutputStream
- DataOutputStream
- PrintStream
2. 字符流
Reader
- InputStreamReader
- FileReader
- BufferedReader
- CharArrayReader
- PipedReader
- StringReader
Writer
- OutputStreamWriter
- FileWriter
- BufferedWriter
- CharArrayWriter
- FilterWriter
- PipedWriter
- PrintWriter
- StringWriter
四、常用类
1. FileInputStream
方法介绍
- read() 方法:当文件读取完成后方法会结束,返回 -1
--->即我们可以通过接收返回值(整型)来判断文件是否读取完成
- close()方法:读取文件数据完成后,用于关闭资源
- close()方法的使用会抛出异常,需要捕获或抛出
注意点
- 该FileInputStream类的创建会抛出异常,需要捕获或抛出
- 操作完成后需要使用 close()方法,以免浪费资源
(1)读取字符
java
public class newFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file.txt";
int readData = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; // 定义为全局变量,方便在后续使用
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
System.out.print("文本的内容是:" );
while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) { // 边读边写
System.out.print((char)readData);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 输出如下
文本的内容是:hello,world代码分析
- 由于 read() 方法返回的是一个整数,然而我们的目的是读取字符,所以在输出的时候强转为 char 类型
- 两个异常需要捕获或者抛出
- 创建 FileInputStream 对象
- 调用 close()方法
- 缺点分析:一个一个字符的读取效率稍低,可以使用读取字符串数组的方式,一次性读取多个字符,提高读取效率
(2)读取数组
java
public class newFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file.txt";
int readLength = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[8]; // 依次读取八个字符
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; // 定义为全局变量,方便在后续使用
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
System.out.print("文本的内容是:" );
while ((readLength = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) { // 边读边写
System.out.print(new String(buf,0,readLength));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 输出如下
文本的内容是:hello,world代码分析
- FileInputStream 读取的是字节流,所以创建 byte[]数组,代码中创建的数组大小为八,即一次性读取八个字节
- 由于读取过程中可能会导致最后的内容不满八个字节,为了不遗漏信息,用 readLen 来接收读取的字符,确保所有信息都会被读取
- 最后输出时调用 String 的构造器,表示把这个数组中规定范围的字符转为字符串,然后输出
2. FileOutputStream
两种构造器
- new FileOutputStream(filePath) 创建方式,当写入内容是,会覆盖原来的内容
- new FileOutputStream(filePath, true) 创建方式,当写入内容是,是追加到文件后面
方法介绍
write() 方法:文件中写入内容
- 写入一个字符
- 写入字符串
注意
- write(字符串数组,左区间,右区间(取不到))
- 指定写入字符串时:区间是左闭右开的
- close()方法:读取文件数据完成后,用于关闭资源
- close()方法的使用会抛出异常,需要捕获或抛出
- 补充方法:getBytes(),将字符串直接转为字符串数组
注意点
- 该FileOutputStream类的创建会抛出异常,需要捕获或抛出
- 操作完成后需要使用 close()方法,以免浪费资源
写入字符
java
public class newFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
fileOutputStream.write('!');
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}代码分析
- 调用了 write() 方法写入了一个感叹号
! - 两个异常需要捕获或者抛出
- 创建 FileOutputStream 对象
- 调用 close()方法
写入字符串
调用 getBytes() 方法把字符串转成字符串数组
java
public class newFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
// 采用追加的方式写入,不会覆盖先前的内容
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath,true);
String str = "hello,world!";
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());// 写入整个字符串
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(),0,5); // 写入字符串指定内容
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}代码分析
- 首先调用 getBytes() 方法把字符串转成字符串数组
- 使用两钟不同的方法是写入字符串
- 写入整个字符串
- 写入字符串中的指定内容(注意:区间是左闭右开)
应用:文件拷贝
题目要求:结合 FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream 实现文件的拷贝
思路
- 使用输入流读取文件信息
- 使用输出流实现文件拷贝
代码示例
java
public class newFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file.txt"; // 源文件路径
String dirpath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file2.txt"; // 目标文件路径
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(dirpath);
int readLen = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[8]; // 一次性读八个字符,提高读取效率
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1){ // 首先读入内容
fileOutputStream.write(buf,0,readLen); // 把读入的内容写到文件中
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭流
try {
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}3. FileReader
说明:FileReader 和 FileWriter 与上面两种类似,区别就在于一个是字节流,一个是字符流,字符流可以读取汉字,不会出现乱码

代码示例
(1)读取单个字符
java
public class newFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
try {
int data;
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
while((data = fileReader.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)data); // 输出的字符,但是read方法接收的是整数
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}代码分析
- reader 是字符流,需要采用 char 数据类型(字节流采用的是 byte)
- read 方法接收的是整数,需要转成字符输出
(2)读取字符串数组
java
public class newFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int readLen = 0;
char[] buf = new char[8]; // 字符流,应该是 char 类型,一次性读取八个字符
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
while((readLen = fileReader.read(buf)) != -1){ // 返回的是实际读取的字符数
System.out.print(new String(buf,0,readLen)); // 输出的字符,但是read方法接收的是整数
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}代码分析
- 通过构建字符串数组,提高读取效率
- 通过 readlen 来记录每次读取的长度,转成字符串输出
4. FileWriter

代码示例
(1)写入字符
java
public class newFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file.txt"; // 源文件路径
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath,true); // 追加方式写入,不会覆盖内容
fileWriter.write("好");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 一定要关闭流才可以实现内容写入
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}代码分析:以追加的方式写入一个字符
(2)写入字符串和字符串数组
java
public class newFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file.txt"; // 源文件路径
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
String str = "非常好";
char[] s = {'a','b','c'};
try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath,true); // 追加方式写入,不会覆盖内容
fileWriter.write(str);
fileWriter.write(s);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 一定要关闭流才可以实现内容写入
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}(3)写入字符串的指定内容
注意:写入指定内容需要转成字符串数组,来指定区间,左闭右开
java
public class newFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\jackson\\Desktop\\file.txt"; // 源文件路径
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
String str = "吃饭了没";
char[] s = {'a','b','c'};
try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath,true); // 追加方式写入,不会覆盖内容
fileWriter.write(str.toCharArray(),0,2);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 一定要关闭流才可以实现内容写入
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}