异常(Exception)
基本介绍
在 Java 程序中,将运行中发生的不正常情况称为 “异常”
异常的分类
Error(错误)
Error 是 Java 虚拟机无法解决的严重问题,同时也是系统级的错误,程序无法处理
举例
(1)JVM 虚拟机的崩溃、虚拟机内存溢出等 “严重” 问题
(2)比如:StackOverflowError(栈溢出)和 OutOfMemoryError(内存溢出)等
Exception(异常)
其他因编程错误或偶然的外在因素导致的一般性问题,可以使用针对性的代码进行处理。例如:空指针异常、数组越界异常、文件找不到异常等
1. 编译异常
编译时异常,是编译器要求必须处理的异常。
2. 运行异常
(1)运行时异常,编译器检查不出来。一般是指编程时的逻辑错误,是程序员应该避免其出现的异常
(2)对于运行时异常,可以不作处理,因为这类异常很普遍,若全处理可能会对程序的可读性和运行效率产生影响
自定义异常
程序出现了某些"错误",但该错误信息并没有在 Throwable 子类中描述处理,这个时候可以自己设计异常类,自定义异常的描述信息
异常体系图
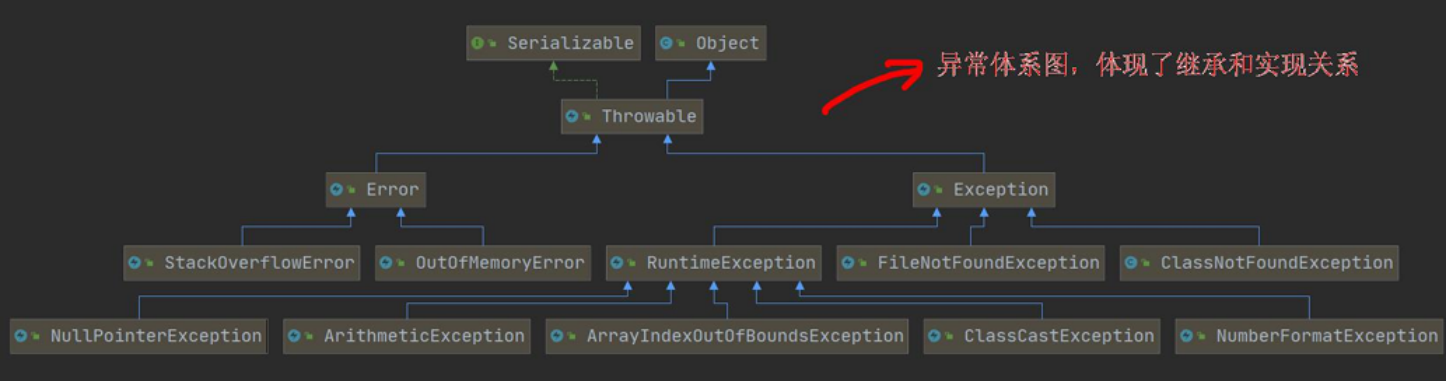
Trowable 的两个子类
(1)Error
(2)Exception
Exception 的两个子类
以下列出的异常例子都是常见的异常
1. 编译异常
(1)ClassNotFoundException
(2)FileNotFoundException
2. 运行异常(RuntimeException)
(1)NullPointerException:空指针异常
(2)ArithmeticException:数学运算异常
(3)ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:数组下标越界异常
(4)ClassCastException:类型转换异常
(5)NumberFormatException:数字格式不正确异常
编译异常
基本介绍
编译异常是指在编译期间,就必须处理的异常,否则代码不能通过编译
常见类型
(1) SQLException:操作数据库时,查询表可能发生异常
(1) IOException:操作文件时,发生的异常
(1) FileNotFoundException:操作一个不存在的文件时,发生异常
(1) ClassNotFoundException:加载类,而该类不存在时,异常
(1) EOFException:操作文件,到文件末尾,发生异常
(1) IllegalArgumentException:参数异常
运行异常
基本介绍
在编译时不会发现,在程序运行时出现的逻辑错误导致的异常,若不做处理,默认抛出(throws)异常,交给 父类 或 上一级 来处理
常见类型
(1) NullPointerException:空指针异常
(2) ArithmeticException:数学运算异常
(3) ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:数组下标越界异常
(4) ClassCastException:类型转换异常
(5) NumberFormatException:数字格式不正确异常
代码示例
空指针异常
NullPointerException 异常:获取空字符窜的长度
java
public class NullPointerException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = null;
System.out.println(name.length());
}
}数学运算异常
ArithmeticException 异常:分母为 0
java
public class ArithmeticException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
System.out.println("a / b = " + a / b);
}
}数组下标越界异常
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:异常:数组只有三个元素,却访问了第四个元素
java
public class ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println("arr[" + i + "] = " + arr[i]);
}
}
}类型转换异常
ClassCastException 异常:A 类 和 B 类 没有关系,不可以把指向 A 类 的对象转成指向 B 类 的对象
java
public class ClassCastException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
person p_a = new A(); // 向上转型
A a = (A)p_a; // 向下转型
// 两个不相关的类进行转换会报异常
B b = (B) p_a; // A 和 B 之间无关系,不可以把指向 A 的转换为 B
}
}
class person {
}
class A extends person{
}
class B extends person{
}数字格式不正确异常
NumberFormatException 异常:无法将字符串转化为整数
java
public class NumberFormatException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "异常";
// 将 String 转成 int
int num = Integer.parseInt(name);
System.out.println(num);
}
}try - catch - finally
快捷键
选中可能出现异常的代码,按 Ctrl + Alt + t,在弹出的内容中选择需要的结构
三大结构
(1)try - catch
(2)try - finally
(3)try - catch - finally
注意:在 catch 结构中,使用 getMessage()方法获取异常信息

代码示例
java
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String name = "异常";
// 将 String 转成 int
int num = Integer.parseInt(name); // 会抛出 NumberFormatException
System.out.println(num);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("程序执行到 finally 部分.....");
}
}
}try - catch 结构
(1)如果发生异常,直接进入到 catch 块,异常所在行后面的代码不会执行
(2)如果没有发生异常,不会进入到 catch,顺序执行 try 的代码块
(3)不管异常是否发生,都希望指向某段代码(比如:关闭连接,释放资源等),可以使用 finally 结构
注意:finally 中的代码一定会执行
(4)可以有多个 catch 语句,捕获不同的异常(进行不同的业务处理)
1. 只会匹配一个 catch
2. 子类异常在前,父类异常在后
多个 catch 结构代码示例
java
package exception_;
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// NullPointerException
String name = null;
System.out.println(name.length());
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println("arr[" + i + "] = " + arr[i]);
}
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常:" + e.getMessage());
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("数组下标越界异常:" + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("程序继续执行......");
}
}
// 运行结果
空指针异常:null
程序继续执行......代码分析
(1)NullPointerException(子类异常)和 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(子类异常)都是 RuntimeException(父类异常)的子类
(2)RuntimeException(运行异常)又是 Exception 的子类
(3)如果把父类 Exception 写在前面(父类异常包含了所有子类异常),后面再写子类异常就没有意义了
try - finally 结构
此结构没有捕获异常,当程序碰到异常时,程序会直接崩掉 / 退出
应用场景
try 中的代码执行完成后,不管是否发生异常,都必须执行某个业务逻辑(finally 部分的代码)
try - catch 练习题
java
public class ExceptionExe01 {
public static int method() {
int i = 1;
try {
i++;
String[] names = new String[3]; // 空指针异常
if (names[1].equals("tom")) {
System.out.println(names[1]);
} else {
names[3] = "jack";
}
return 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 2;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
return ++i;
} finally {
++i;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(method());
}
}
// 输出结果
i = 4
3代码分析
(1)finally 一定会执行,所以在调用方法的时候就执行了其中的代码,调用了 method()方法,输出的肯定是方法的返回值
(2)代码中属于空指针异常,即会在 catch (NullPointerException e)中返回 i 的值
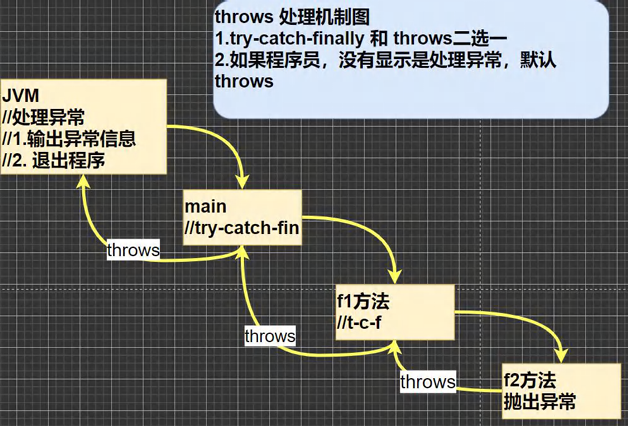
throws
基本介绍
表示抛出异常,不做处理,由上一级或者父类做处理
(1)程序可能出现某些异常,通过 throws 显示的声明,不做处理
(2)在方法声明中用 throws 语句可以声明抛出异常的列表,抛出的异常类型可以是
1. 方法中产生的异常类型
2. 抛出的异常类型的父类
(3)抛出的异常由上一级 / 调用者 / 父类进行处理
(1)上一级做 try - catch 的处理,捕获异常
(2)上一级不做处理,继续抛出异常 throws
注意:如果抛出的是编译异常,上一级必须显示声明异常的处理
(4)如果上一级都不做处理,最后到 JVM 时,会直接结束程序,输出异常信息
原理图
代码示例
(1)抛出方法中的异常
java
public static void method() throws NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{
// NullPointerException
String name = null;
System.out.println(name.length());
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println("arr[" + i + "] = " + arr[i]);
}
System.out.println("程序继续执行......");
}(2)抛出方法中的异常的父类
java
public static void method() throws RuntimeException{
// NullPointerException
String name = null;
System.out.println(name.length());
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println("arr[" + i + "] = " + arr[i]);
}
System.out.println("程序继续执行......");
}代码分析
(1)父类异常:RuntimeException
(2)子类异常: NullPointerException、ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
使用细节
(1) 对于编译异常,程序中必须处理(try-catch 或者 throws)
(2) 对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是 throws 的方式处理
(3) 子类重写父类的方法时,子类重写的方法所抛出异常类型的两种情况
1. 要么类型要和父类抛出的异常一致
2. 要么为父类抛出的异常的类型的子类型
(4) 在 throws 过程中,如果方法 try-catch,就相当于处理异常,就可以不必 throws
代码示例
java
class a {
public void method() throws RuntimeException{
// NullPointerException
String name = null;
System.out.println(name.length());
}
}
class b extends a {
@Override
public void method() throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println("arr[" + i + "] = " + arr[i]);
}
}
}代码分析
(1)b 类是 a 类的子类,则b 类抛出的异常必须是 a 类抛出异常类型的子类,然而 a 类抛出异常的类型 NullPointerException`是 RuntimeException 的子类,抛出的异常类型用其父类代替是没有问题的
(2)若将子类抛出异常的类型换成 Exception,必然会报错,因为扩大了父类抛出异常的类型(本质还是继承关系)
自定义异常(throw)
引入关键字:throw
基本介绍
程序出现了某些"错误",但该错误信息并没有在 throwable 子类中描述处理,这个时候可以自己设计异常类,自定义异常的描述信息
实现方法
定义类,自定义异常类名(程序员自己写),继承 Exception 或 RuntimeException
(1)如果继承 Exception,属于编译时异常(受检异常)
(2)如果继承 RuntimeException,属于运行时异常(非受检异常)
代码示例
接收 person 对象年龄时,要求年龄范围在
18 - 120之间,否则抛出一个自定义异常,并给出提示信息
java
package exception_;
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 180;
if(!(age >= 18 && age <= 120)){
throw new AgeException("年龄需要在 18 - 120 之间");
}
System.out.println("你的年龄范围正确");
}
}
class AgeException extends RuntimeException {
// 调用 RuntimeException 的构造器,修改异常信息
public AgeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}输出结果
java
Exception in thread "main" exception_.AgeException: 年龄需要在 18 - 120 之间
at exception_.main.main(main.java:7)代码分析
创建了一个类,通过调用父类的构造器,在创建自定义异常调用构造器来传入自定义异常信息
如何理解 new?
异常是一个类,抛出的必须是异常类的一个对象实例,所以需要 new,创建对象时通过调用构造器传入信息来完成对象实例的初始化
⭐ 自定义异常信息
throw new RuntimeException("自定义异常信息")
对比 throw 和 throws
| 意义 | 位置 | 后面跟的东西 |
|---|---|---|
| throws | 方法声明处 | 异常类 |
| throw | 方法体中 | 异常对象 |
