三层架构
问题引入
当前程序的这个业务逻辑还是比较简单的,如果业务逻辑再稍微复杂一点,我们会看到 Controller 方法的代码量就很大了
(1)当我们要修改操作数据部分的代码,需要改动 Controller
(2)当我们要完善逻辑处理部分的代码,需要改动 Controller
(3)当我们需要修改数据响应的代码,还是需要改动 Controller
这样呢,就会造成我们整个工程代码的复用性比较差,而且代码难以维护
三大层
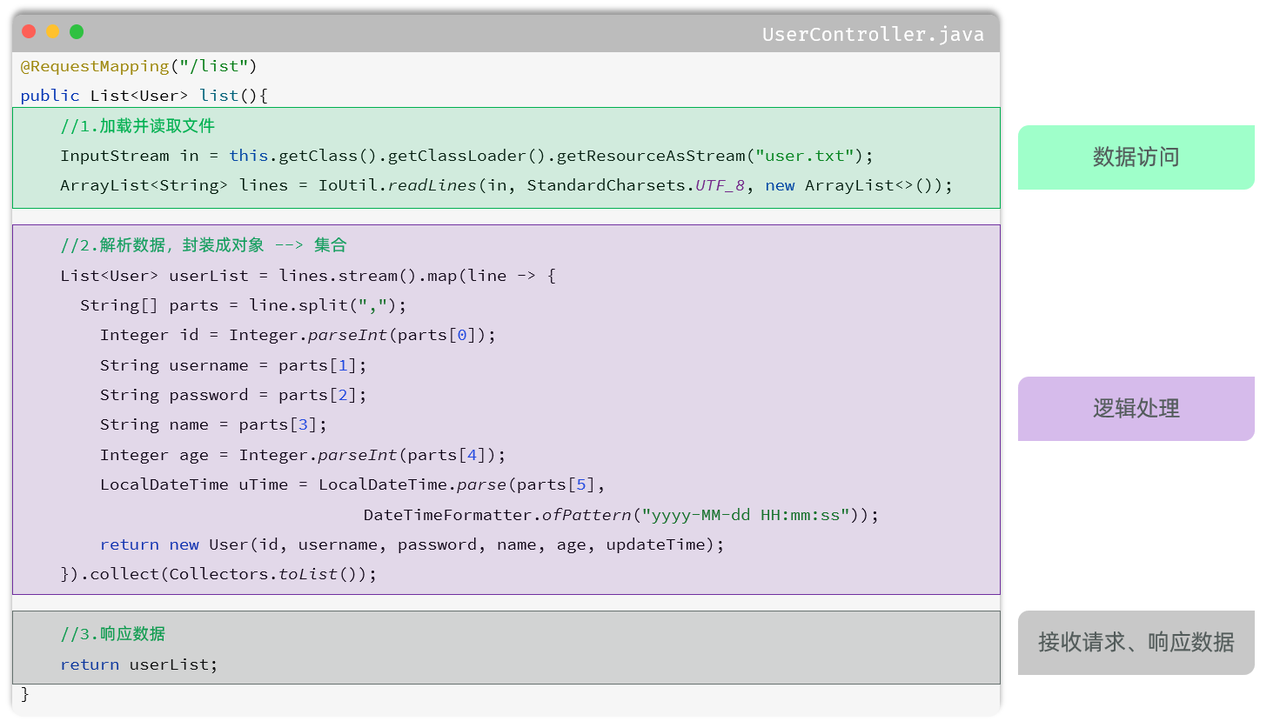
(1)数据访问:负责业务数据的维护操作,包括增、删、改、查等操作
(2)逻辑处理:负责业务逻辑处理的代码
(3)请求处理、响应数据:负责,接收页面的请求,给页面响应数据

(1)Controller:控制层。接收前端发送的请求,对请求进行处理,并响应数据
(2)Service:业务逻辑层。处理具体的业务逻辑
(3)Dao:数据访问层(Data Access Object),也称为持久层。负责数据访问操作,包括数据的增、删、改、查
调用逻辑
(1)前端发起的请求,由 Controller 层接收(Controller 响应数据给前端)
(2)Controller 层调用 Service 层来进行逻辑处理(Service 层处理完后,把处理结果返回给 Controller 层)
(3)Serivce 层调用 Dao 层(逻辑处理过程中需要用到的一些数据要从 Dao 层获取)
(4)Dao 层操作文件中的数据(Dao 拿到的数据会返回给 Service 层)
三大优势
(1)复用性强
(2)便于维护
(3)利用扩展
案例代码分层
Controller 层
控制层:接收前端发送的请求,对请求进行处理,并响应数据
在 com.itheima.controller 中创建 UserController 类,代码如下
java
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.pojo.User;
import com.itheima.service.UserService;
import com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class UserController {
private UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
@RequestMapping("/list")
public List<User> list(){
//1.调用Service
List<User> userList = userService.findAll();
//2.响应数据
return userList;
}
}Service 层
业务逻辑层:处理具体的业务逻辑
在 com.itheima.service 中创建 UserSerivce 接口,代码如下
java
package com.itheima.service;
import com.itheima.pojo.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserService {
public List<User> findAll();
}在 com.itheima.service.impl 中创建 UserSerivceImpl 接口,代码如下
java
package com.itheima.service.impl;
import com.itheima.dao.UserDao;
import com.itheima.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl;
import com.itheima.pojo.User;
import com.itheima.service.UserService;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
@Override
public List<User> findAll() {
List<String> lines = userDao.findAll();
List<User> userList = lines.stream().map(line -> {
String[] parts = line.split(",");
Integer id = Integer.parseInt(parts[0]);
String username = parts[1];
String password = parts[2];
String name = parts[3];
Integer age = Integer.parseInt(parts[4]);
LocalDateTime updateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(parts[5], DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
return new User(id, username, password, name, age, updateTime);
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return userList;
}
}Dao 层
数据访问层:负责数据的访问操作,包含数据的增、删、改、查
在 com.itheima.dao 中创建 UserDao 接口,代码如下
java
package com.itheima.dao;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserDao {
public List<String> findAll();
}在 com.itheima.dao.impl 中创建 UserDaoImpl 接口,代码如下
java
package com.itheima.dao.impl;
import cn.hutool.core.io.IoUtil;
import com.itheima.dao.UserDao;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public List<String> findAll() {
InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("user.txt");
ArrayList<String> lines = IoUtil.readLines(in, StandardCharsets.UTF_8, new ArrayList<>());
return lines;
}
}