Spring Cache 框架
基本介绍
Spring Cache 是一个缓存框架,只需要简单地加一个注解,就能实现缓存功能
Spring Cache 提供了一层抽象,底层可以切换不同的缓存实现,例如: EHCache、Caffeine、Redis(常用)
Macen 依赖坐标
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>常用注解
Spring Cache 注解生效的前提:在启动类上使用 @EnableCaching 开启缓存支持

代码示例
@EnableCaching
在启动类上使用 @EnableCaching 开启缓存支持,Spring Cache 注解才能生效
java
package com.itheima;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching // 开启缓存注解功能
public class CacheDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CacheDemoApplication.class,args);
log.info("项目启动成功...");
}
}注解参数
每一个注解都有两个属性:cacheNames(或者 value)、key
cacheNames(value):指定缓存的名称。缓存的名称相当于缓存文件夹的名称,所有与这个名称相关的缓存数据都会被存储在这个缓存中。一个缓存名称可以包含多个缓存项,每个缓存项通过不同的 key 来区分
key:用于指定缓存项的唯一标识符。每个缓存数据都会有一个与之相关的 key,通过这个 key 可以存取缓存中的数据。key 可以是方法参数,也可以是一个自定义的表达式来决定如何生成缓存的键,支持 Spring 的表达式语言 SPEL 语法
最终的数据格式 --> cacheNames :: key
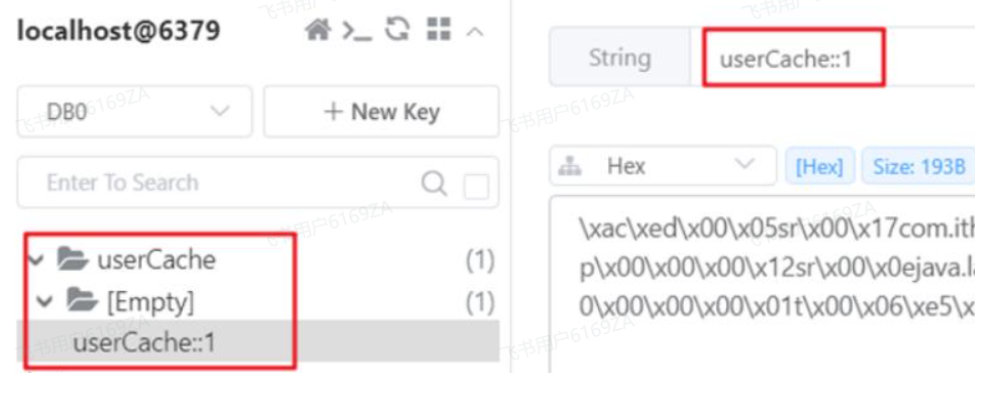
⭐ Key 的写法(SPEL)
#user.id : #user 指的是方法形参的名称,id 指的是 user 的 id 属性,也就是使用 user 的 id 属性作为 key(推荐写法)
#result.id : #result 代表方法的返回值,该表达式代表以返回对象的 id 属性作为 key
#p0.id:#p0 指的是方法中的第一个参数,id 指的是第一个参数的 id 属性,也就是使用第一个参数的 id 属性作为 key
#a0.id:#a0 指的是方法中的第一个参数,id 指的是第一个参数的 id 属性,也就是使用第一个参数的 id 属性作为 key
#root.args[0].id:#root.args[0]指的是方法中的第一个参数,id 指的是第一个参数的 id 属性,也就是使用第一个参数的 id 属性作为 key
@Cacheable
作用:在方法执行前,spring 先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据,若没有数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中
(1)单个查询参数
java
@GetMapping
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache",key="#id")
public User getById(Long id){
User user = userMapper.getById(id);
return user;
}(2)多个查询参数
例如分页查询,每一条数据可以根据特定的字段唯一标识,这也可以作为一条记录缓存
在 Dto 中重写 hashCode 方法,指定唯一标识数据的字段,返回 hash 值,若 hash 值相同,说明查询的正是这条数据,直接从缓存中返回即可
由于查询条件查询的结果为空,所以需要加上unless 参数,否则缓存中存储太多无意义的数据
java
// ServiceImpl
@Cacheable(value = "userCache",key="#userDto.hashCode()",unless = "#result.size() == 0")
public List<User> getList(UserDto userDto){
List<User> list = userMapper.getList("%" + userDto.getName() + "%", userDto.getAge());
return list;
}
// dto
@Data
public class UserDto {
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = Objects.hash(getName(),getAge());
return result;
}
}@CachePut
作用: 将方法返回值,放入缓存,一般保存的时候使用该注解
java
@PostMapping
@CachePut(value = "userCache", key = "#user.id") // key的生成:userCache::1
public User save(@RequestBody User user){
userMapper.insert(user);
return user;
}@CacheEvict
作用:清理指定缓存
allEntries = true:删除缓存中的所有数据
key:用于指定要删除的缓存项的 key
java
@DeleteMapping
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "userCache",key = "#id") // 删除某个 key 对应的缓存数据
public void deleteById(Long id){
userMapper.deleteById(id);
}
@DeleteMapping("/delAll")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "userCache",allEntries = true) // 删除 userCache 下所有的缓存数据
public void deleteAll(){
userMapper.deleteAll();
}@Caching
作用:组装其他缓存注解
cacheable:组装一个或多个 @Cacheable 注解
put:组装一个或多个 @CachePut 注解
evict:组装一个或多个 @CacheEvict 注解
java
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(value = "userCache",key = "#id")
},
put = {
@CachePut(value = "userCache",key = "#result.name"),
@CachePut(value = "userCache",key = "#result.age")
}
)
public User insert(User user){
userMapper.insert(user);
return user;
}自定义序列化方式
类似于 RedisTemplate 实现缓存,如果需要使得 Redis 中的数据格式更直观,可以自定义序列方式
默认是二进制数据格式,可以转为字符换、json 数据格式
java
package com.zzyl.config;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericToStringSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {
// 启用 JSON 存储格式
@Bean
public CacheManager jsonCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
// 使用 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer 作为值的序列化器
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer =
new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
// 创建 RedisCacheConfiguration,设置默认的序列化策略
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(redisCacheConfiguration)
.build();
}
// 二进制数据存储
@Bean
public CacheManager binaryCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
// 使用 GenericToStringSerializer 作为二进制数据序列化器
GenericToStringSerializer<Object> binarySerializer =
new GenericToStringSerializer<>(Object.class);
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(binarySerializer));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(redisCacheConfiguration)
.build();
}
// 字符串存储
@Bean
public CacheManager stringCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
// 使用 StringRedisSerializer 作为值的序列化器
StringRedisSerializer stringSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(stringSerializer));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(redisCacheConfiguration)
.build();
}
}